Effect of NHE1 antisense gene transfection on the biological behavior of SGC-7901 human gastric carcinoma cells
- PMID: 18407588
- PMCID: PMC2703839
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2162
Effect of NHE1 antisense gene transfection on the biological behavior of SGC-7901 human gastric carcinoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To study the effect of type 1 Na(+)/H(+) exchanger (NHE1) antisense human gene transfection on the biological behavior of gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901.
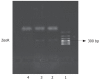
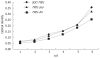
Methods: Antisense NHE1 eukaryotic expression on vector pcDNA3.1 was constructed by recombinant DNA technique and transfected into gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901 with DOTAP liposome transfection method. Morphological changes of cells were observed with optic and electron microscopes. Changes in cell proliferative capacity, apoptosis, intracellular pH (pH(i)), cell cycle, clone formation in two-layer soft agar, and tumorigenicity in nude mice were examined.
Results: Antisense eukaryotic expressing vectors were successfully constructed and transfected into SGC-7901. The transfectant obtained named 7901-antisense (7901-AS) stablely produced antisense NHE1. There was a significant difference between the pH(i) of 7901-AS cells (6.77 +/- 0.05) and that of 7901-zeo cells and SGC-7901 cells (7.24 +/- 0.03 and 7.26 +/- 0.03, P < 0.01). Compared with SGC-7901 and 7901-zeo cells, 7901-AS cells mostly showed cell proliferation inhibition, G1/G0 phase arrest, increased cell apoptotic rate, recovery of contact inhibition, and density contact. The tumorigenicity in nude mice and cloning efficiency in the two-layer soft agar were clearly inhibited.
Conclusion: NHE1 antisense gene significantly restrains the malignant behavior of human gastric carcinoma cells, suppresses cell growth and induces cell apoptosis, and partially reverses the malignant phenotypes of SGC-7901. These results suggest a potential role for human tumor gene therapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of antisense human telomerase RNA on malignant phenotypes of gastric carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Nov;17(11):1144-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02857.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 12453272
-
Antisense human telomerase reverse transcriptase could partially reverse malignant phenotypes of gastric carcinoma cell line in vitro.Eur J Cancer Prev. 2008 Jun;17(3):209-17. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0b013e3282b71f0d. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2008. PMID: 18414191
-
NHE1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Oncol Rep. 2017 Mar;37(3):1451-1460. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5386. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28098891
-
[Effects of inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by RNA interference on proliferation and apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells: an experimental study with human gastric cancer cells and mice].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Jan 24;86(4):266-71. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16677508 Chinese.
-
Voltage-gated sodium channel Nav 1.7 promotes gastric cancer progression through MACC1-mediated upregulation of NHE1.Int J Cancer. 2016 Dec 1;139(11):2553-69. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30381. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27529686
Cited by
-
The Role of Plasma Membrane Sodium/Hydrogen Exchangers in Gastrointestinal Functions: Proliferation and Differentiation, Fluid/Electrolyte Transport and Barrier Integrity.Front Physiol. 2022 May 18;13:899286. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.899286. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35665228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotensin signaling induces intracellular alkalinization and interleukin-8 expression in human pancreatic cancer cells.Mol Oncol. 2009 Jun;3(3):204-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2009.01.006. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Mol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19393580 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration and dysfunction of ion channels/transporters in a hypoxic microenvironment results in the development and progression of gastric cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Aug;44(4):739-749. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00604-1. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33856653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(Patho-)Physiology of Na+/H+ Exchangers (NHEs) in the Digestive System.Front Physiol. 2020 Jan 15;10:1566. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01566. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32009977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological role of ion channels and transporters in gastrointestinal mucosal diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8109-8125. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04011-5. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34778915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Slepkov E, Fliegel L. Structure and function of the NHE1 isoform of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;80:499–508. - PubMed
-
- Malo ME, Fliegel L. Physiological role and regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;84:1081–1095. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen SF. The Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 in stress-induced signal transduction: implications for cell proliferation and cell death. Pflugers Arch. 2006;452:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Reshkin SJ, Bellizzi A, Cardone RA, Tommasino M, Casavola V, Paradiso A. Paclitaxel induces apoptosis via protein kinase A- and p38 mitogen-activated protein-dependent inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) NHE isoform 1 in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:2366–2373. - PubMed
-
- Teng XC, Liu HF, Liu YS, Duan L, Wang GA, He JT. Expression of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 in gastric carcinoma and precancerous lesions and its clinical significance. Acta Academiae Med. Militaris Tertiae. 2004;26:402–404.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

