Effects of estradiol and progesterone on the proinflammatory cytokine production by mononuclear cells from patients with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 18407594
- PMCID: PMC2703845
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2200
Effects of estradiol and progesterone on the proinflammatory cytokine production by mononuclear cells from patients with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of estradiol (E2) and progesterone on the unstimulated and oxidative stress-stimulated production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-8, and macrophage chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with chronic hepatitis C and healthy controls.
Methods: The PBMCs were separated from age-matched 72 males and 71 females with and without chronic hepatitis C, who were divided into two groups based on a mean menopausal age of 50 years. Oxidative stress was induced by hydrogen peroxide in the cells incubated in serum-free media. Cytokines in the culture supernatant were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
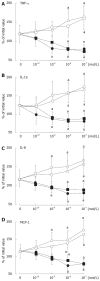
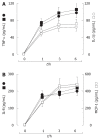
Results: The highest levels of the spontaneous production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-8, and MCP-1 by the unstimulated PBMCs were in the older male patients with chronic hepatitis C and the lowest levels were in the pre-menopausal female healthy controls. E2 inhibited the cytokine production by the unstimulated PBMCs from the older male and post-menopausal female patients, which was further stimulated by progesterone. The exposure to hydrogen peroxide in the PBMCs from the younger male and pre-menopausal female healthy subjects induced the production of cytokines. The change rates of the hydrogen peroxide-stimulated cytokine production were suppressed by E2 and enhanced by progesterone.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that E2 may play a favorable role in the course of persistent liver injury by preventing the accumulation of monocytes-macrophages and by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokine production, whereas progesterone may counteract the favorable E2 effects.
Figures
References
-
- McMahon BJ, Alberts SR, Wainwright RB, Bulkow L, Lanier AP. Hepatitis B-related sequelae. Prospective study in 1400 hepatitis B surface antigen-positive Alaska native carriers. Arch Intern Med. 1990;150:1051–1054. - PubMed
-
- Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Goodman Z, McHutchison J, Albrecht J. Rates and risk factors of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis c. J Hepatol. 2001;34:730–739. - PubMed
-
- Pfeilschifter J, Koditz R, Pfohl M, Schatz H. Changes in proinflammatory cytokine activity after menopause. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:90–119. - PubMed
-
- Pinkus R, Weiner LM, Daniel V. Role of oxidants and antioxidants in the induction of AP-1, NF-kappaB, and glutathione S-transferase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13422–13429. - PubMed
-
- Omoya T, Shimizu I, Zhou Y, Okamura Y, Inoue H, Lu G, Itonaga M, Honda H, Nomura M, Ito S. Effects of idoxifene and estradiol on NF-kappaB activation in cultured rat hepatocytes undergoing oxidative stress. Liver. 2001;21:183–191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

