The Aeromonas hydrophila wb*O34 gene cluster: genetics and temperature regulation
- PMID: 18408022
- PMCID: PMC2446748
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00153-08
The Aeromonas hydrophila wb*O34 gene cluster: genetics and temperature regulation
Abstract
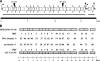
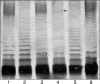
The Aeromonas hydrophila wb*(O34) gene cluster of strain AH-3 (serotype O34) was cloned and sequenced. This cluster contains genes necessary for the production of O34-antigen lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in A. hydrophila. We determined, using either mutation or sequence homology, roles for the majority of genes in the cluster by using the chemical O34-antigen LPS structure obtained for strain AH-3. The O34-antigen LPS export system has been shown to be a Wzy-dependent pathway typical of heteropolysaccharide pathways. Furthermore, the production of A. hydrophila O34-antigen LPS in Escherichia coli K-12 strains is dependent on incorporation of the Gne enzyme (UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase) necessary for the formation of UDP-galactosamine in these strains. By using rapid amplification of cDNA ends we were able to identify a transcription start site upstream of the terminal wzz gene, which showed differential transcription depending on the growth temperature of the strain. The Wzz protein is able to regulate the O34-antigen LPS chain length. The differential expression of this protein at different temperatures, which was substantially greater at 20 degrees C than at 37 degrees C, explains the previously observed differential production of O34-antigen LPS and its correlation with the virulence of A. hydrophila serotype O34 strains.
Figures
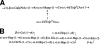

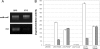

Similar articles
-
Role of Gne and GalE in the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila serotype O34.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jan;189(2):540-50. doi: 10.1128/JB.01260-06. Epub 2006 Nov 10. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17098903 Free PMC article.
-
The UDP N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase gene is essential for mesophilic Aeromonas hydrophila serotype O34 virulence.Infect Immun. 2006 Jan;74(1):537-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.537-548.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16369010 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and chemical analysis of the lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila strain AH-1 (Serotype O11).Mar Drugs. 2015 Apr 14;13(4):2233-49. doi: 10.3390/md13042233. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25874921 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of three Aeromonas hydrophila AH-3 (serotype O34) lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis gene clusters.J Bacteriol. 2008 May;190(9):3176-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.01874-07. Epub 2008 Feb 29. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18310345 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Gne (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-4-epimerase), Wzz (chain length determinant), and Wzy (O-antigen polymerase) of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:8.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(15):4277-87. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.15.4277-4287.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12107146 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aeromonas surface glucan attached through the O-antigen ligase represents a new way to obtain UDP-glucose.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035707. Epub 2012 May 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563467 Free PMC article.
-
Aeromonas hydrophila flagella glycosylation: involvement of a lipid carrier.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):e89630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089630. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 May 9;20(5):e0324165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324165. PMID: 24586923 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The main Aeromonas pathogenic factors.ISRN Microbiol. 2012 Sep 4;2012:256261. doi: 10.5402/2012/256261. Print 2012. ISRN Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23724321 Free PMC article.
-
Melanization and pathogenicity in the insect, Tenebrio molitor, and the crustacean, Pacifastacus leniusculus, by Aeromonas hydrophila AH-3.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 29;5(12):e15728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015728. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21206752 Free PMC article.
-
Haemophilus parainfluenzae expresses diverse lipopolysaccharide O-antigens using ABC transporter and Wzy polymerase-dependent mechanisms.Int J Med Microbiol. 2013 Dec;303(8):603-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24035104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allard, S. T. M., M.-F. Giraud, C. Whitfield, M. Graninger, P. Messner, and J. H. Naismith. 2001. The crystal structure of dTDP-d-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (RmlB) from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, the second enzyme in the dTDP-l-rhamnose pathway. J. Mol. Biol. 307283-295. - PubMed
-
- Artsimovitch, I., and R. Landick. 2002. The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell 109193-203. - PubMed
-
- Austin, B., and C. Adams. 1996. Fish pathogens, p. 197-243. In B. Austin, M. Altwegg, P. J. Gosling, and S. W. Joseph (ed.), The genus Aeromonas. John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

