Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins
- PMID: 18408713
- PMCID: PMC5434866
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.83
Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins
Abstract
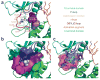
Necroptosis is a cellular mechanism of necrotic cell death induced by apoptotic stimuli in the form of death domain receptor engagement by their respective ligands under conditions where apoptotic execution is prevented. Although it occurs under regulated conditions, necroptotic cell death is characterized by the same morphological features as unregulated necrotic death. Here we report that necrostatin-1, a previously identified small-molecule inhibitor of necroptosis, is a selective allosteric inhibitor of the death domain receptor-associated adaptor kinase RIP1 in vitro. We show that RIP1 is the primary cellular target responsible for the antinecroptosis activity of necrostatin-1. In addition, we show that two other necrostatins, necrostatin-3 and necrostatin-5, also target the RIP1 kinase step in the necroptosis pathway, but through mechanisms distinct from that of necrostatin-1. Overall, our data establish necrostatins as the first-in-class inhibitors of RIP1 kinase, the key upstream kinase involved in the activation of necroptosis.
Figures
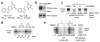
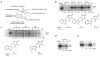
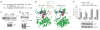
References
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
-
- Lindsten T, Thompson CB. Cell death in the absence of Bax and Bak. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:1272–1276. - PubMed
-
- Los M, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K. The role of caspases in development, immunity, and apoptotic signal transduction: lessons from knockout mice. Immunity. 1999;10:629–639. - PubMed
-
- Chautan M, Chazal G, Cecconi F, Gruss P, Golstein P. Interdigital cell death can occur through a necrotic and caspase-independent pathway. Curr Biol. 1999;9:967–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

