Increased apoptotic potential and dose-enhancing effect of gold nanoparticles in combination with single-dose clinical electron beams on tumor-bearing mice
- PMID: 18410403
- PMCID: PMC11158140
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00827.x
Increased apoptotic potential and dose-enhancing effect of gold nanoparticles in combination with single-dose clinical electron beams on tumor-bearing mice
Abstract
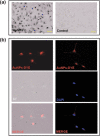
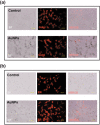
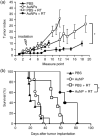
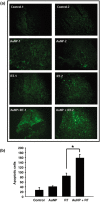
High atomic number material, such as gold, may be used in conjunction with radiation to provide dose enhancement in tumors. In the current study, we investigated the dose-enhancing effect and apoptotic potential of gold nanoparticles in combination with single-dose clinical electron beams on B16F10 melanoma tumor-bearing mice. We revealed that the accumulation of gold nanoparticles was detected inside B16F10 culture cells after 18 h of incubation, and moreover, the gold nanoparticles were shown to be colocalized with endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in cells. Furthermore, gold nanoparticles radiosensitized melanoma cells in the colony formation assay (P = 0.02). Using a B16F10 tumor-bearing mouse model, we further demonstrated that gold nanoparticles in conjunction with ionizing radiation significantly retarded tumor growth and prolonged survival compared to the radiation alone controls (P < 0.05). Importantly, an increase of apoptotic signals was detected inside tumors in the combined treatment group (P < 0.05). Knowing that radiation-induced apoptosis has been considered a determinant of tumor responses to radiation therapy, and the length of tumor regrowth delay correlated with the extent of apoptosis after single-dose radiotherapy, these results may suggest the clinical potential of gold nanoparticles in improving the outcome of melanoma radiotherapy.
Figures


References
-
- Matsudaira H, Ueno AM, Furuno I. Iodine contrast medium sensitizes cultured mammalian cells to X rays but not to gamma rays. Radiat Res 1980; 84: 144–8. - PubMed
-
- Das IJ, Chopra KL. Backscatter dose perturbation in kilovoltage photon beams at high atomic number interfaces. Med Phys 1995; 22: 767–73. - PubMed
-
- Das IJ. Forward dose perturbation at high atomic number interfaces in kilovoltage x‐ray beams. Med Phys 1997; 24: 1781–7. - PubMed
-
- Verhaegen F, Reniers B, Deblois F et al . Dosimetric and microdosimetric study of contrast‐enhanced radiotherapy with kilovolt x‐rays. Phys Med Biol 2005; 50: 3555–69. - PubMed
-
- Werner BL, Das IJ, Salk WN. Dose perturbations at interfaces in photon beams: secondary electron transport. Med Phys 1990; 17: 212–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

