Special article: chronic granulomatous disease in the United Kingdom and Ireland: a comprehensive national patient-based registry
- PMID: 18410635
- PMCID: PMC2384093
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03644.x
Special article: chronic granulomatous disease in the United Kingdom and Ireland: a comprehensive national patient-based registry
Abstract
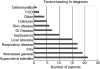
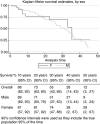
There are no epidemiological studies from the British Isles of chronic granulomatous disease, characterized by recurrent, life-threatening bacterial and fungal infections and inflammatory sequelae. Patients were enrolled in a national registry and medical records were analysed. Of 94 subjects, 69 had X-linked disease, 16 had autosomal recessive disease and nine were unknown. Prevalence was 7.5/million for 1990-99 and 8.5/million for 1980-89. Suppurative adenitis, abscesses and pneumonia presented commonly. Twenty-three of 30 patients who underwent high resolution computerized tomography had chronic respiratory disease. Inflammatory sequelae included bowel stricture and urogenital tract granulomata. Growth failure was common; 75% of those measured were below the population mean. All patients received prophylactic antibiotics and 93% anti-fungal prophylaxis. Interferon gamma was used to treat infection, but rarely as prophylaxis. Despite prophylaxis, estimated survival was 88% at 10 years but 55% at age 30 years. Morbidity remains significant, severe infectious complications common. Curative treatments including stem cell transplantation should be considered for patients with frequent or serious complications.
Figures
References
-
- Berendes H, Bridges RA, Good RA. A fatal granulomatosus of childhood. Minn Med. 1957;40:309–12. - PubMed
-
- Landing BH, Shirkey HA. A syndrome of recurrent infection and infiltration of viscera by pigmented lipid histiocytes. Pediatrics. 1957;20:431–8. - PubMed
-
- Segal AW, Peters TJ. Characterisation of the enzyme defect in chronic granulomatous disease. Lancet. 1976;1:1363–5. - PubMed
-
- Curnutte JT, Whitten D, Babior BM. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974;290:593–7. - PubMed
-
- Dinauer MC, Orkin SH, Brown R, Jesaitis AJ, Parkos CA. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. Nature. 1987;327:717–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical