Placenta growth factor augments endothelin-1 and endothelin-B receptor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha
- PMID: 18411415
- PMCID: PMC2481529
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-130567
Placenta growth factor augments endothelin-1 and endothelin-B receptor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha
Abstract
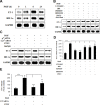
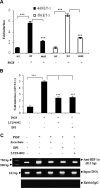
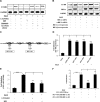
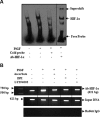
Pulmonary hypertension (PHT) develops in sickle cell disease (SCD) and is associated with high mortality. We previously showed that erythroid cells produce placenta growth factor (PlGF), which activates monocytes to induce proinflammatory cytochemokines, contributing to the baseline inflammation and severity in SCD. In this study, we observed that PlGF increased expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelin-B receptor (ET-BR) from human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMVECs) and monocytes, respectively. PlGF-mediated ET-1 and ET-BR expression occurred via activation of PI-3 kinase, reactive oxygen species and hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1 alpha). PlGF increased binding of HIF-1 alpha to the ET-1 and ET-BR promoters; this effect was abrogated with mutation of hypoxia response elements in the promoter regions and HIF-1 alpha siRNA and confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. Furthermore, PlGF-mediated ET-1 release from HPMVECs and ET-BR expression in monocytes creates a PlGF-ET-1-ET-BR loop, leading to increased expression of MCP-1 and IL-8. Our studies show that PlGF-induced expression of the potent vasoconstrictor ET-1 and its cognate ET-BR receptor occur via activation of HIF-1 alpha, independent of hypoxia. PlGF levels are intrinsically elevated from the increased red cell turnover in SCD and in other chronic anemia (eg, thalassemia) and may contribute to inflammation and PHT seen in these diseases.
Figures

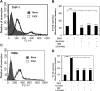
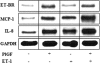
Comment in
-
It really IS the red cell.Blood. 2008 Aug 1;112(3):459-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-155754. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18650459 No abstract available.
References
-
- Francis RB, Jr., Johnson CS. Vascular occlusion in sickle cell disease: current concepts and unanswered questions. Blood. 1991;77:1405–1414. - PubMed
-
- Platt OS, Thorington BD, Brambilla DJ, et al. Pain in sickle cell disease. Rates and risk factors. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan G R. Infection. In: Embury SH, Hebbel RP, Mohandas N, Steinberg MH, editors. Sickle Cell Disease—Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. New York: Raven Press; 1994. pp. 567–587.
-
- Wong WY, Powars DR, Chan L, et al. Polysaccharide encapsulated bacterial infection in sickle cell anemia: a thirty year epidemiologic experience. Am J Hematol. 1992;39:176–182. - PubMed
-
- Embury S H, Hebbel R P, Steinberg M H, Mohandas N. Pathogenesis of vasoocclusion. In: Embury SH, Hebbel RP, Mohandas N, Steinberg MH, editors. Sickle Cell Disease—Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. New York: Raven Press; 1994. pp. 311–326.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

