Serum urate as a predictor of clinical and radiographic progression in Parkinson disease
- PMID: 18413464
- PMCID: PMC2574855
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.2008.65.6.nct70003
Serum urate as a predictor of clinical and radiographic progression in Parkinson disease
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether concentration of serum urate, a purine metabolite and potent antioxidant that has been linked to a reduced risk of Parkinson disease (PD), predicts prognosis in PD.
Design: Prospective study.
Setting: The Parkinson Research Examination of CEP-1347 Trial (PRECEPT) study, which investigated the effects of a potential neuroprotectant on rates of PD progression, was conducted between April 2002 and August 2005 (average follow-up time 21.4 months).
Participants: Eight hundred four subjects with early PD enrolled in the PRECEPT study.
Main outcome measures: The primary study end point was progression to clinical disability sufficient to warrant dopaminergic therapy. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) of reaching end point according to quintiles of baseline serum urate concentration, adjusting for sex, age, and other potential covariates. Change in striatal uptake of iodine I 123-labeled 2-beta-carbomethoxy-3-beta-(4-iodophenyl)tropane ([(123)I]beta-CIT), a marker for the presynaptic dopamine transporter, was assessed with linear regression for a subset of 399 subjects.
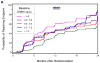
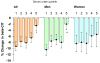
Results: The adjusted HR of reaching end point declined with increasing baseline concentrations of urate; subjects in the top quintile reached the end point at only half the rate of subjects in the bottom quintile (HR, 0.51; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.37-0.72; P for trend < .001). This association was markedly stronger in men (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.26-0.60; P for trend < .001) than in women (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.39-1.50; P for trend = .33). The percentage of loss in striatal [(123)I]beta-CIT uptake also improved with increasing serum urate concentrations (overall P for trend = .002; men, P = .001; women, P = .43).
Conclusions: These findings identify serum urate as the first molecular factor directly linked to the progression of typical PD and suggest that targeting urate or its determinants could be an effective disease-modifying therapy in PD. Trial Registration clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00040404.
Figures

Comment in
-
Serum uric acid and clinical progression in Parkinson disease: potential biomarker for nigrostriatal failure.Arch Neurol. 2008 Jun;65(6):698-9. doi: 10.1001/archneur.65.6.698. Arch Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18541788 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oda M, Satta Y, Takenaka O, Takahata N. Loss of urate oxidase activity in hominoids and its evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol. 2002 May;19(5):640–653. - PubMed
-
- Jenner P. Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2003;53 Suppl 3:S26–36. S36–28. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Mitochondria take center stage in aging and neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol. 2005 Oct;58(4):495–505. - PubMed
-
- Davis JW, Grandinetti A, Waslien CI, Ross GW, White LR, Morens DM. Observations on serum uric acid and the risk of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;144:480–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

