More than one way to skin .
- PMID: 18413712
- PMCID: PMC2732395
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1645908
More than one way to skin .
Abstract
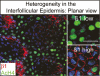
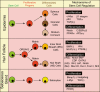
Epithelial stem cells in the skin are specified during development and are governed by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions to differentially adopt the cell fates that enable them to form the epidermis, hair follicle, and sebaceous gland. In the adult, each of three epithelial lineages maintains their own stem cell population for self-renewal and normal tissue homeostasis. However, in response to injury, at least some of these stem cell niches can be mobilized to repair an epithelial tissue whose resident stem cells have been damaged. How do these stem cell populations respond to multiple signaling networks, activate migration, and proliferation, and differentiate along a specific lineage? Recent clues add new pieces to this multidimensional puzzle. Understanding how these stem cells maintain normal homeostasis and wound repair in the skin is particularly important, as these mechanisms, when defective, lead to skin tissue diseases including cancers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Designer skin: lineage commitment in postnatal epidermis.Trends Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;12(4):185-92. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)02263-8. Trends Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11978538 Review.
-
Human skin stem cells and the ageing process.Exp Gerontol. 2008 Nov;43(11):986-97. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2008.09.001. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Exp Gerontol. 2008. PMID: 18809487 Review.
-
Building epithelial tissues from skin stem cells.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:333-50. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.032. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008. PMID: 19022769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lgr6 marks stem cells in the hair follicle that generate all cell lineages of the skin.Science. 2010 Mar 12;327(5971):1385-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1184733. Science. 2010. PMID: 20223988
-
Epithelial stem cells and implications for wound repair.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Dec;23(9):946-53. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23085626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond acne: Current aspects of sebaceous gland biology and function.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016 Sep;17(3):319-334. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9389-5. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27726049 Review.
-
Natural corneal cell-based microenvironment as prerequisite for balanced 3D corneal epithelial morphogenesis: a promising animal experiment-abandoning tool in ophthalmology.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014 Apr;20(4):297-307. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2013.0195. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014. PMID: 23886248 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type-specific differentiation and molecular profiles in skin transplantation: implication of medical approach for genetic skin diseases.J Transplant. 2011;2011:501857. doi: 10.1155/2011/501857. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Transplant. 2011. PMID: 22174987 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of trachebronchial tissue-specific stem cell pool size.Stem Cells. 2013 Dec;31(12):2767-78. doi: 10.1002/stem.1440. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23712882 Free PMC article.
-
A functional role of RB-dependent pathway in the control of quiescence in adult epidermal stem cells revealed by genomic profiling.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010 Jun;6(2):162-77. doi: 10.1007/s12015-010-9139-0. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010. PMID: 20376578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atit R., Conlon R.A., Niswander L. EGF signaling patterns the feather array by promoting the interbud fate. Dev. Cell. 2003;4:231–240. - PubMed
-
- Blanpain C., Lowry W.E., Geoghegan A., Polak L., Fuchs E. Self-renewal, multipotency, and the existence of two cell populations within an epithelial stem cell niche. Cell. 2004;118:635–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
