Sorafenib inhibits growth and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in malignant peripheral nerve sheath cells
- PMID: 18413802
- PMCID: PMC3267321
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0518
Sorafenib inhibits growth and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in malignant peripheral nerve sheath cells
Abstract
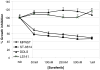
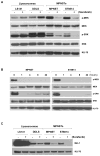
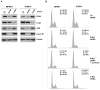
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) are soft-tissue tumors with a very poor prognosis and largely resistant to chemotherapy. MPNSTs are characterized by activation of the Ras pathway by loss of tumor suppressor neurofibromatosis type 1. In view of this, MPNST may be susceptible to inhibition of the activated Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by the B-Raf inhibitor sorafenib. MPNST (MPNST and ST8814) and dedifferentiated liposarcoma (LS141 and DDLS) human tumor cell lines were characterized for Ras activation and B-Raf expression. Tumor cells were treated with sorafenib and examined for growth inhibition, inhibition of phospho-MEK, phospho-ERK, cell cycle arrest, and changes in cyclin D1 and pRb expression. MPNSTs were sensitive to sorafenib at nanomolar concentrations. This appeared to be due to inhibition of phospho-MEK, phospho-ERK, suppression of cyclin D1, and hypophosphorylation of pRb at the CDK4-specific sites, resulting in a G(1) cell cycle arrest. These effects were not seen in the liposarcoma cells, which either did not express B-Raf or showed decreased Ras activation. Small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of B-Raf in MPNSTs also induced a G(1) cell cycle arrest in these cells, with a marked inhibition of cyclin D1 expression and Rb phosphorylation, whereas depletion of C-Raf did not affect either. With growth inhibition at the low nanomolar range, sorafenib, by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, may prove to be a novel therapy for patients with MPNST.
Figures


References
-
- Clark MA, Fisher C, Judson I, Thomas JM. Soft tissue sarcomas in adults. NEJM. 2005;353:701–711. - PubMed
-
- Zwick E, Bange J, Ullrich A. Receptor tyrosine kinases as targets for anticancer drugs. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:472–480. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;64(19):7099–109. - PubMed
-
- Chang F, Steelman LS, Lee JT, et al. Signal transduction mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway from cytokine receptors to transcription factors: potential targeting for therapeutic intervention. Leukemia. 2003;17:1263–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

