Mathematical modeling of pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 18414484
- PMCID: PMC2387229
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2008.17
Mathematical modeling of pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
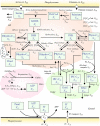
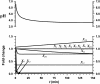
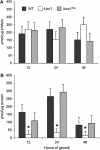
Cryptococcus neoformans (Cn) is the most common cause of fungal meningitis worldwide. In infected patients, growth of the fungus can occur within the phagolysosome of phagocytic cells, especially in non-activated macrophages of immunocompromised subjects. Since this environment is characteristically acidic, Cn must adapt to low pH to survive and efficiently cause disease. In the present work, we designed, tested, and experimentally validated a theoretical model of the sphingolipid biochemical pathway in Cn under acidic conditions. Simulations of metabolic fluxes and enzyme deletions or downregulation led to predictions that show good agreement with experimental results generated post hoc and reconcile intuitively puzzling results. This study demonstrates how biochemical modeling can yield testable predictions and aid our understanding of fungal pathogenesis through the design and computational simulation of hypothetical experiments.
Figures

References
-
- Achleitner G, Gaigg B, Krasser A, Kainersdorfer E, Kohlwein SD, Perktold A, Zellnig G, Daum G (1999) Association between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of yeast facilitates interorganelle transport of phospholipids through membrane contact. Eur J Biochem 264: 545–553 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez M, Casadevall A (2006) Phagosome extrusion and host-cell survival after Cryptococcus neoformans phagocytosis by macrophages. Curr Biol 16: 2161–2165 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

