ROCK1 mediates leukocyte recruitment and neointima formation following vascular injury
- PMID: 18414683
- PMCID: PMC2293333
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29226
ROCK1 mediates leukocyte recruitment and neointima formation following vascular injury
Abstract
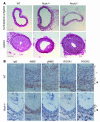
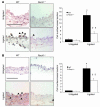
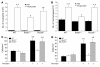
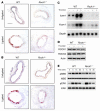
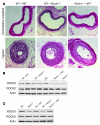
Although Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) activity has been implicated in cardiovascular diseases, the tissue- and isoform-specific roles of ROCKs in the vascular response to injury are not known. To address the role of ROCKs in this process, we generated haploinsufficient Rock1 (Rock1(+/-)) and Rock2 (Rock2(+/-)) mice and performed carotid artery ligations. Following this intervention, we found reduced neointima formation in Rock1(+/-) mice compared with that of WT or Rock2(+/-) mice. This correlated with decreased vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival, decreased levels proinflammatory adhesion molecule expression, and reduced leukocyte infiltration. In addition, thioglycollate-induced peritoneal leukocyte recruitment and accumulation were substantially reduced in Rock1(+/-) mice compared with those of WT and Rock2(+/-) mice. To determine the role of leukocyte-derived ROCK1 in neointima formation, we performed reciprocal bone marrow transplantation (BMT) in WT and Rock1(+/-) mice. Rock1(+/-) to WT BMT led to reduced neointima formation and leukocyte infiltration following carotid ligation compared with those of WT to WT BMT. In contrast, WT to Rock1(+/-) BMT resulted in increased neointima formation. These findings indicate that ROCK1 in BM-derived cells mediates neointima formation following vascular injury and suggest that ROCK1 may represent a promising therapeutic target in vascular inflammatory diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Tanaka H., et al. Sustained activation of vascular cells and leukocytes in the rabbit aorta after balloon injury. Circulation. 1993;88:1788–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM067049/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL053993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-67283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL052233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-67249/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067249/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL053993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM-67049/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062729/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL080187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070274/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

