Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease
- PMID: 18415116
- PMCID: PMC2413111
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0424-9
Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease
Abstract
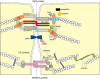
Tight junctions create a paracellular barrier in epithelial and endothelial cells protecting them from the external environment. Two different classes of integral membrane proteins constitute the tight junction strands in epithelial cells and endothelial cells, occludin and members of the claudin protein family. In addition, cytoplasmic scaffolding molecules associated with these junctions regulate diverse physiological processes like proliferation, cell polarity and regulated diffusion. In many diseases, disruption of this regulated barrier occurs. This review will briefly describe the molecular composition of the tight junctions and then present evidence of the link between tight junction dysfunction and disease.
Figures
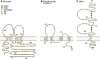
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16371949', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16371949/'}]}
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Review. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:41–53 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2115479', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2115479/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2568363', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2568363/'}]}
- Achler C, Filmer D, Merte C, Drenckhahn D (1989) Role of microtubules in polarized delivery of apical membrane proteins to the brush border of the intestinal epithelium. J Cell Biol 109:179–189 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11698262', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11698262/'}]}
- Ahdieh M, Vandenbos T, Youakim A (2001) Lung epithelial barrier function and wound healing are decreased by IL-4 and IL-13 and enhanced by IFN-gamma. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C2029–C2038 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2120780', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2120780/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8601611', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8601611/'}]}
- Ando-Akatsuka Y, Saitou M, Hirase T, Kishi M, Sakakibara A, Itoh M, Yonemura S, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1996) Interspecies diversity of the occludin sequence: cDNA cloning of human, mouse, dog, and rat-kangaroo homologues. J Cell Biol 133:43–47 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9836530', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9836530/'}]}
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW (1998) Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content: vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothelial cells. Penn State Retina Research Group. Diabetes 47:1953–1959 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

