Cytokine-producing B lymphocytes-key regulators of immunity
- PMID: 18417336
- PMCID: PMC2474694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.03.003
Cytokine-producing B lymphocytes-key regulators of immunity
Abstract
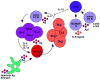
The successful use of B cell depletion therapy for the treatment of autoimmune disease has led to a resurgent appreciation of B cells as powerful regulators of immunity. However, to the surprise of many, B cells appear to regulate autoimmune conditions independently of their ability to produce autoantibodies. Indeed, disturbances in the ability of B cell subsets to present antigen, produce cytokines, and regulate the activities of T cells is emerging as a key feature in many inflammatory diseases. Here we review the recent literature describing cytokine-producing regulatory and effector B cell subsets in health and disease and discuss how future B cell-directed therapies might target the pathologic cytokine-producing effector B cell subsets without impacting the protective regulatory subsets.
Figures


References
-
- Sanz I, Anolik JH, Looney RJ. B cell depletion therapy in autoimmune diseases. Front Biosci. 2007;12:2546–2567. An excellent review highlighting the clinical effects of B cell depletion therapy and discussing the antibody dependent and independent roles of B cells in immune responses. - PubMed
-
- Lund FE, Garvy BA, Randall TD, Harris DP. Regulatory roles for cytokine-producing B cells in infection and autoimmune disease. Curr Dir Autoimmunity. 2005;8:25–54. - PubMed
-
- Mizoguchi A, Bhan AK. A case for regulatory B cells. J Immunol. 2006;176:705–710. The most comprehensive review of regulatory B cell biology. - PubMed
-
- Pistoia V. Production of cytokines by human B cells in health and disease. Immunol Today. 1997;18:343–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

