Cell-type-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of the herpes simplex virus tegument protein VP11/12 encoded by gene UL46
- PMID: 18417566
- PMCID: PMC2447066
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02121-07
Cell-type-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of the herpes simplex virus tegument protein VP11/12 encoded by gene UL46
Abstract
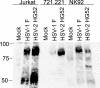
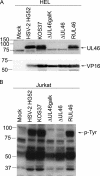
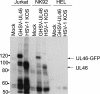
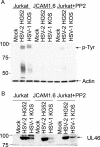
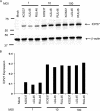
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells play key roles in limiting herpesvirus infections; consequently, many herpesviruses, including herpes simplex virus (HSV), have evolved diverse strategies to evade and/or disarm these killer lymphocytes. Previous studies have shown that CTL and NK cells are functionally inactivated following contact with HSV-infected fibroblasts. During studies of the mechanisms involved, we discovered that HSV-inactivated NK-92 NK cells and Jurkat T cells contain a strikingly prominent, novel, ca. 90-kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein that we identified as the HSV tegument protein VP11/12. Inasmuch as VP11/12 produced in fibroblasts and epithelial cells is not obviously tyrosine phosphorylated, these data suggested that VP11/12 serves as the substrate of a cell-type-specific protein tyrosine kinase. Consistent with this hypothesis, VP11/12 was also tyrosine phosphorylated in B lymphocytes, and this modification was severely reduced in Jurkat T cells lacking the lymphocyte-specific Src family kinase Lck. These findings demonstrate that HSV tegument proteins can be differentially modified depending on the cell type infected. Our data also raise the possibility that VP11/12 may modulate one or more lymphocyte-specific signaling pathways or serve another lymphocyte-specific function. However, HSV type 1 mutants lacking the UL46 gene retained the ability to block signaling through the T-cell receptor in Jurkat cells and remained competent to functionally inactivate the NK-92 NK cell line, indicating that VP11/12 is not essential for lymphocyte inactivation. Further studies are therefore required to determine the biological function of tyrosine-phosphorylated VP11/12.
Figures
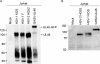



References
-
- Ambagala, A. P., J. C. Solheim, and S. Srikumaran. 2005. Viral interference with MHC class I antigen presentation pathway: the battle continues. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1071-15. - PubMed
-
- Arnon, T. I., G. Markel, and O. Mandelboim. 2006. Tumor and viral recognition by natural killer cells receptors. Semin. Cancer Biol. 16348-358. - PubMed
-
- Aubert, M., E. M. Krantz, and K. R. Jerome. 2006. Herpes simplex virus genes Us3, Us5, and Us12 differentially regulate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced cytotoxicity. Viral Immunol. 19391-408. - PubMed
-
- Benedict, C. A., P. S. Norris, and C. F. Ware. 2002. To kill or be killed: viral evasion of apoptosis. Nat. Immunol. 31013-1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

