Apolipoprotein D is involved in the mechanisms regulating protection from oxidative stress
- PMID: 18419796
- PMCID: PMC2574913
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00395.x
Apolipoprotein D is involved in the mechanisms regulating protection from oxidative stress
Abstract
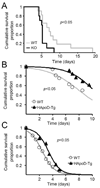
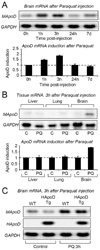
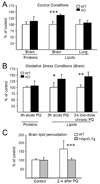
Many nervous system pathologies are associated with increased levels of apolipoprotein D (ApoD), a lipocalin also expressed during normal development and aging. An ApoD homologous gene in Drosophila, Glial Lazarillo, regulates resistance to stress, and neurodegeneration in the aging brain. Here we study for the first time the protective potential of ApoD in a vertebrate model organism. Loss of mouse ApoD function increases the sensitivity to oxidative stress and the levels of brain lipid peroxidation, and impairs locomotor and learning abilities. Human ApoD overexpression in the mouse brain produces opposite effects, increasing survival and preventing the raise of brain lipid peroxides after oxidant treatment. These observations, together with its transcriptional up-regulation in the brain upon oxidative insult, identify ApoD as an acute response protein with a protective and therefore beneficial function mediated by the control of peroxidated lipids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human ApoD, an apolipoprotein up-regulated in neurodegenerative diseases, extends lifespan and increases stress resistance in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 May 13;105(19):7088-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800896105. Epub 2008 May 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18458334 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein D mediates autocrine protection of astrocytes and controls their reactivity level, contributing to the functional maintenance of paraquat-challenged dopaminergic systems.Glia. 2011 Oct;59(10):1551-66. doi: 10.1002/glia.21200. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21688324
-
Sex-dependent modulation of longevity by two Drosophila homologues of human Apolipoprotein D, GLaz and NLaz.Exp Gerontol. 2011 Jul;46(7):579-89. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2011.02.014. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Exp Gerontol. 2011. PMID: 21376794
-
Apolipoprotein D takes center stage in the stress response of the aging and degenerative brain.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Jul;35(7):1632-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.01.148. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24612673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein D.Gene. 2020 Sep 25;756:144874. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144874. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32554047 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular Unit-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: From Their Physiopathological Roles to Their Clinical Applications in Acute Brain Injuries.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 1;10(9):2147. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092147. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Pattern of Myelin-Related Apolipoprotein D in Human Multiple Sclerosis Lesions.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Aug 21;10:254. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00254. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30186153 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Apolipoprotein D levels in human pregnancy and association with gestational weight gain.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009 Sep 2;7:92. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-92. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19723339 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein D alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteogenesis suppression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Aug 8;15(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01824-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32771037 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of protein carbonyls in plasma, cell extracts, tissue homogenates, isolated proteins: Focus on sample preparation and derivatization conditions.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:367-380. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26141921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akerstrom B, Borregaard N, Flower DR, Salier J-P, editors. Lipocalins. Georgetown, Texas: Landes Biosciences; 2006.
-
- Akerstrom B, Maghzal G, Winterbourn CC, Kettle AJ. The lipocalin alpha 1-microglobulin has radical scavenger activity. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:31493–31503. - PubMed
-
- Allhorn M, Berggard T, Nordberg J, Olsson ML, Akerstrom B. Processing of the lipocalin alpha(1)-microglobulin by hemoglobin induces heme-binding and heme-degradation properties. Blood. 2002;99:1894–1901. - PubMed
-
- Allhorn M, Klapyta A, Akerstrom B. Redox properties of the lipocalin alpha1-microglobulin: reduction of cytochrome c, hemoglobin, and free iron. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Balboa MA, Balsinde J. Oxidative stress and arachidonic acid mobilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:385–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

