A musculoskeletal model of the upper extremity for use in the development of neuroprosthetic systems
- PMID: 18420213
- PMCID: PMC2586642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.03.001
A musculoskeletal model of the upper extremity for use in the development of neuroprosthetic systems
Abstract
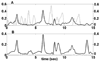
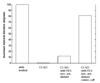
Upper extremity neuroprostheses use functional electrical stimulation (FES) to restore arm motor function to individuals with cervical level spinal cord injury. For the design and testing of these systems, a biomechanical model of the shoulder and elbow has been developed, to be used as a substitute for the human arm. It can be used to design and evaluate specific implementations of FES systems, as well as FES controllers. The model can be customized to simulate a variety of pathological conditions. For example, by adjusting the maximum force the muscles can produce, the model can be used to simulate an individual with tetraplegia and to explore the effects of FES of different muscle sets. The model comprises six bones, five joints, nine degrees of freedom, and 29 shoulder and arm muscles. It was developed using commercial, graphics-based modeling and simulation packages that are easily accessible to other researchers and can be readily interfaced to other analysis packages. It can be used for both forward-dynamic (inputs: muscle activation and external load; outputs: motions) and inverse-dynamic (inputs: motions and external load; outputs: muscle activation) simulations. Our model was verified by comparing the model calculated muscle activations to electromyographic signals recorded from shoulder and arm muscles of five subjects. As an example of its application to neuroprosthesis design, the model was used to demonstrate the importance of rotator cuff muscle stimulation when aiming to restore humeral elevation. It is concluded that this model is a useful tool in the development and implementation of upper extremity neuroprosthetic systems.
Figures




References
-
- Charlton IW, Johnson GR. An interactive musculoskeletal model of the upper limb; Proceedings of the 3rd Conference of the International Shoulder Group; Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. 2000.
-
- de Groot JH, Brand R. A three-dimensional regression model of the shoulder rhythm”. Clinical Biomechanics. 2001;16:735–743. - PubMed
-
- DeLuca CJ, Forrest WJ. Force analysis of individual muscles acting simultaneously on the shoulder during isometric abduction. Journal of Biomechanics. 1973;6:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Dul J. Shoulder muscle load during work with elevated arms; Proceedings of the 11th International Congress in Biomechanics; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1987.
-
- Hodges PW, Bui BH. A comparison of computer-based methods for the determination of onset of muscle contraction using electromyography. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology. 1996;101:511–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

