Artificial dural sealant that allows multiple penetrations of implantable brain probes
- PMID: 18420281
- PMCID: PMC2570645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.02.018
Artificial dural sealant that allows multiple penetrations of implantable brain probes
Abstract
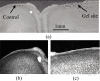
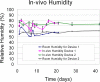
This study reports extensive characterization of the silicone gel (3-4680, Dow Corning, Midland, MI), for potential use as an artificial dural sealant in long-term electrophysiological experiments in neurophysiology. Dural sealants are important to preserve the integrity of the intracranial space after a craniotomy and in prolonging the lifetime and functionality of implanted brain probes. In this study, we report results of our tests on a commercially available silicone gel with unique properties that make it an ideal dural substitute. The substitute is transparent, elastic, easy to apply, and has re-sealing capabilities, which makes it desirable for applications where multiple penetrations by the brain probe is desirable over an extended period of time. Cytotoxicity tests (for up to 10 days) with fibroblasts and in vivo tests (for 12 weeks) show that the gel is non-toxic and does not produce any significant neuronal degeneration when applied to the rodent cortex even after 12 weeks. In vivo humidity testing showed no sign of CSF leakage for up to 6 weeks. The gel also allows silicon microprobes to penetrate with forces less than 0.5 mN, and a 200-microm diameter stainless steel microprobe with a blunt tip to penetrate with a force less than 2.5 mN. The force dependency on the velocity of penetration and thickness of the gel was also quantified and empirically modeled. The above results demonstrate that the silicone gel (3-4680) can be a viable dural substitute in long-term electrophysiology of the brain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Experimental study on the mechanical interaction between silicon neural microprobes and rat dura mater during insertion.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015 Feb;26(2):70. doi: 10.1007/s10856-015-5401-y. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015. PMID: 25631267
-
Single neuronal recordings using surface micromachined polysilicon microelectrodes.J Neurosci Methods. 2005 Mar 15;142(1):45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.07.017. J Neurosci Methods. 2005. PMID: 15652616
-
A microfabricated, 3D-sharpened silicon shuttle for insertion of flexible electrode arrays through dura mater into brain.J Neural Eng. 2019 Oct 29;16(6):066021. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab2b2e. J Neural Eng. 2019. PMID: 31216526 Free PMC article.
-
Dural sealants for the management of cerebrospinal fluid leakage after intradural surgery: current status and future perspectives.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019 Jul;16(7):549-553. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2019.1626232. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019. PMID: 31144544 Review.
-
The use of dural sealant patches for reinforcement of durotomy repair: a systematic review.Neurosurg Focus. 2025 Feb 1;58(2):E11. doi: 10.3171/2024.12.FOCUS24705. Neurosurg Focus. 2025. PMID: 39891941
Cited by
-
Flow of cortical activity underlying a tactile decision in mice.Neuron. 2014 Jan 8;81(1):179-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.020. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24361077 Free PMC article.
-
Application of PLGA/type I collagen/chitosan artificial composite dura mater in the treatment of dural injury.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013 Sep;24(9):2247-54. doi: 10.1007/s10856-013-4964-8. Epub 2013 Jul 6. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013. PMID: 23832452
-
Large-scale imaging of cortical dynamics during sensory perception and behavior.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Jun 1;115(6):2852-66. doi: 10.1152/jn.01056.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26912600 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropixels Opto: Combining high-resolution electrophysiology and optogenetics.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 21:2025.02.04.636286. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.04.636286. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975326 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
In Vivo Electrochemical Analysis of a PEDOT/MWCNT Neural Electrode Coating.Biosensors (Basel). 2015 Oct 13;5(4):618-46. doi: 10.3390/bios5040618. Biosensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26473938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arieli A, Grinvald A, Slovin H. Dural substitute for long-term imaging of cortical activity in behaving monkeys and its clinical implications. J Neurosci Meth. 2002;114:119–33. - PubMed
-
- Baker SN, Philbin N, Spinks R, Pinches EM, Wolpert DM, MacManus DG, Pauluis Q, Lemon RN. Multiple single unit recording in the cortex of monkeys using independently moveable microelectrodes. J Neurosci Meth. 1999;94:5–17. - PubMed
-
- Becker TA, Kipke DR. Algel as dural sealant, determination of effects on the sensorimotor cortex in rats.. 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS: Cancun; Mexico. 2003: 1972−5.
-
- Beltramino C, de Olmos J, Gallyas F, Heimer L, Zabroszky L. Silver staining as a tool for neurotoxic assessment. NIDA Res Monogr. 1993;136:101–25. - PubMed
-
- Green J. A simple microelectrode for recording from the central nervous system. Nature. 1958;182:962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

