Monotone Signal Segments Analysis as a novel method of breath detection and breath-to-breath interval analysis in rat
- PMID: 18420469
- PMCID: PMC2517178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2008.03.001
Monotone Signal Segments Analysis as a novel method of breath detection and breath-to-breath interval analysis in rat
Abstract
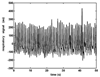
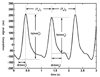
We applied a novel approach to respiratory waveform analysis--Monotone Signal Segments Analysis (MSSA) on 6-h recordings of respiratory signals in rats. To validate MSSA as a respiratory signal analysis tool we tested it by detecting: breaths and breath-to-breath intervals; respiratory timing and volume modes; and changes in respiratory pattern caused by lesions of monoaminergic systems in rats. MSSA differentiated three respiratory timing (tachypneic, eupneic, bradypneic-apneic), and three volume (artifacts, normovolemic, hypervolemic-sighs) modes. Lesion-induced respiratory pattern modulation was visible as shifts in the distributions of monotone signal segment amplitudes, and of breath-to-breath intervals. Specifically, noradrenergic lesion induced an increase in mean volume (p<or=0.03), with no change of the mean breath-to-breath interval duration (p>or=0.06). MSSA of timing modes detected noradrenergic lesion-induced interdependent changes in the balance of eupneic (decrease; p<or=0.02), and tachypneic (an increase; p<or=0.02) breath intervals with respect to control. In terms of breath durations within each timing mode, there was a tendency toward prolongation of the eupneic (p<or=0.08) and bradypneic-apneic (p<or=0.06) intervals. These results demonstrate that MSSA is sensitive to subtle shifts in respiratory rhythmogenesis not detectable by simple respiratory pattern descriptive statistics. MSSA represents a potentially valuable new tool for investigations of respiratory pattern control.
Figures






References
-
- Benchetrit G. Breathing pattern in humans: diversity and individuality. Respir Physiol. 2000;122:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Bertinieri G, di Rienzo M, Cavalazzi A, Ferrari AU, Pedotti A, Mancia G. Evaluation of baroreceptor reflex by blood pressure monitoring in unanesthetized cats. Am J Physiol. 1988;254:H377–H383. - PubMed
-
- Carley DW. Minimal modeling of hyman respiratory stability. In: Khoo M, editor. Modeling and parameter estimation in respiratory control. NY: Plenum Press; 1989. pp. 171–180.
-
- Carley DW, Maayan C, Grimes J, Shannon DC. Breath-by-breath respiratory timing and volume control during periodic breathing. Am J Physiol. 1989;257:R653–R660. - PubMed
-
- Carley DW, Radulovacki M. Mirtazapine, a mixed-profile serotonin agonist/antagonist, suppresses sleep apnea in the rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:1824–1829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

