O-GlcNAc regulates FoxO activation in response to glucose
- PMID: 18420577
- PMCID: PMC2423255
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802240200
O-GlcNAc regulates FoxO activation in response to glucose
Abstract
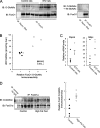
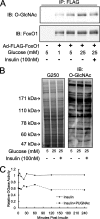
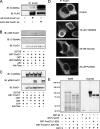
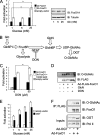
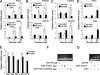
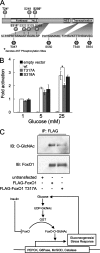
FoxO proteins are key transcriptional regulators of nutrient homeostasis and stress response. The transcription factor FoxO1 activates expression of gluconeogenic, including phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase, and also activates the expression of the oxidative stress response enzymes catalase and manganese superoxide dismutase. Hormonal and stress-dependent regulation of FoxO1 via acetylation, ubiquitination, and phosphorylation, are well established, but FoxOs have not been studied in the context of the glucose-derived O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification. Here we show that O-GlcNAc on hepatic FoxO1 is increased in diabetes. Furthermore, O-GlcNAc regulates FoxO1 activation in response to glucose, resulting in the paradoxically increased expression of gluconeogenic genes while concomitantly inducing expression of genes encoding enzymes that detoxify reactive oxygen species. GlcNAcylation of FoxO provides a new mechanism for direct nutrient control of transcription to regulate metabolism and stress response through control of FoxO1 activity.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang, W., Patil, S., Chauhan, B., Guo, S., Powell, D. R., Le, J., Klotsas, A., Matika, R., Xiao, X., Franks, R., Heidenreich, K. A., Sajan, M. P., Farese, R. V., Stolz, D. B., Tso, P., Koo, S. H., Montminy, M., and Unterman, T. G. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 10105–10117 - PubMed
-
- Puig, O., and Tjian, R. (2006) Cell Cycle 5 503–505 - PubMed
-
- Lehtinen, M. K., Yuan, Z., Boag, P. R., Yang, Y., Villen, J., Becker, E. B., DiBacco, S., de la Iglesia, N., Gygi, S., Blackwell, T. K., and Bonni, A. (2006) Cell 125 987–1001 - PubMed
-
- Tothova, Z., Kollipara, R., Huntly, B. J., Lee, B. H., Castrillon, D. H., Cullen, D. E., McDowell, E. P., Lazo-Kallanian, S., Williams, I. R., Sears, C., Armstrong, S. A., Passegue, E., DePinho, R. A., and Gilliland, D. G. (2007) Cell 128 325–339 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

