Effects of switching between anti-TNF therapies on HAQ response in patients who do not respond to their first anti-TNF drug
- PMID: 18420660
- PMCID: PMC2430221
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken127
Effects of switching between anti-TNF therapies on HAQ response in patients who do not respond to their first anti-TNF drug
Abstract
Objectives: Small studies have shown an improvement in disease activity in patients with RA who have switched between anti-TNF therapies for reasons of inefficacy. However, it is not clear whether switching improves longer term outcomes, such as disability. This analysis compares changes in HAQ scores 1 yr following lack of response to a first anti-TNF based on subsequent treatment during that year.
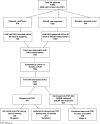
Methods: Analysis was limited to RA patients with inefficacy to a first anti-TNF based on (i) clinician opinion and/or (ii) disease activity score in 28 joints and had an HAQ measured at time of non-response and 12 months later. Patients were classified into three groups based on treatment during the next 12 months: (i) continued anti-TNF despite non-response; (ii) stopped anti-TNF with no further biologics; and (iii) switched to a second anti-TNF. Mean improvement in HAQ was compared among the groups using multivariable linear regression models.
Results: As of July 2006, 868 patients met the inclusion for this analysis. Four hundred and seventy-nine patients stopped anti-TNF of whom 331 switched to a second anti-TNF. Three hundred and eighty-nine continued treatment. Patients who continued and those who switched had improvements in HAQ over the 12 months, unlike patients who discontinued all biologic therapy. The best improvement was seen in those who switched [adjusted mean improvement in HAQ 0.15 (95% CI 0.26, 0.05)].
Conclusion: There is a significant improvement in HAQ in patients who switch to a second anti-TNF, providing an effective next choice of therapy for some patients who fail to respond to their first anti-TNF.
References
-
- Lipsky PE, Van der Heijde DMFM, St Clair EW, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1594–602. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, et al. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:253–9. - PubMed
-
- Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, et al. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1586–93. - PubMed
-
- Hyrich KL, Symmons DP, Watson KD, Silman AJ. Comparison of the response to infliximab or etanercept monotherapy with the response to cotherapy with methotrexate or another disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1786–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous