An assessment of fixed-capacity models of visual working memory
- PMID: 18420818
- PMCID: PMC2329704
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711295105
An assessment of fixed-capacity models of visual working memory
Abstract
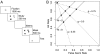
Visual working memory is often modeled as having a fixed number of slots. We test this model by assessing the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) of participants in a visual-working-memory change-detection task. ROC plots yielded straight lines with a slope of 1.0, a tell-tale characteristic of all-or-none mnemonic representations. Formal model assessment yielded evidence highly consistent with a discrete fixed-capacity model of working memory for this task.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Osaka N, Logie RH, D'Esposito M. The Cognitive Neuroscience of Working Memory. Oxford, UK: Oxford Univ Press; 2007.
-
- Cowan N. The magic number 4 in short-term memory: A reconsideration of Mental Storage Capacity. Behav Brain Sci. 2001;24:87–114. - PubMed
-
- Miyake A, Shah P. Models of Working Memory: Mechanisms of Active Maintenance and Executive Control. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 1999.
-
- Luck SJ, Vogel EK. The capacity of visual working memory for features and conjunctions. Nature. 1997;390:279–281. - PubMed
-
- Miller GA. The magical number seven plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol Rev. 1956;63:81–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

