The versatile reverse flow sural artery neurocutaneous flap: a case series and review of literature
- PMID: 18423034
- PMCID: PMC2373287
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-799X-3-15
The versatile reverse flow sural artery neurocutaneous flap: a case series and review of literature
Abstract
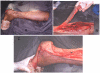
Background: Reverse flow sural neurocutaneous flap has been utilized more frequently during the past decade to cover vital structures around the foot and ankle area. The potential advantages are the relatively constant blood supply, ease of elevation and preservation of major vascular trunks in the leg. The potential disadvantages remain venous congestion, donor site morbidity and lack of sensation.
Methods: This descriptive case series was conducted at Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, from 1997 to 2003. Ten patients having undergone reverse flow sural neurocutaneous flap were identified through medical records. There were six females (60%) and four males (40%), with an average age of 59.8 years. The defects occurred as a result of trauma in five patients (50%), diabetic ulcers in four (40%) and decubitus ulcer in one (10%) paraplegic patient. The defect site included non weight bearing heel in four (40%), tendo Achilles in two (20%), distal tibia in two (20%), lateral malleolus in one (10%) and medial aspect of the midfoot in one patient (10%). The maximum flap size harvested was 14 x 6 cm. Preoperative doppler evaluation was performed in all patients to identify perforators and modified plaster of paris boot was used in the post operative period. A detailed questionnaire was developed addressing variables of interest.
Results: There was no flap failure. Venous congestion was encountered in one case. The donor site was relatively unsightly but acceptable to all patients. The loss of sensation in the sural nerve distribution was transient in all patients.
Conclusion: Reverse sural artery flap remains to be the workhorse flap to resurface the soft tissue defects of the foot and ankle. Anastomosis of the sural nerve to the digital plantar nerve can potentially solve the issue of lack of sensation in the flap especially when used for weight bearing heel.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Comparison between two different repairing methods for skin defects of foot and ankle].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Dec;20(12):1202-4. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17228681 Chinese.
-
A comparison of two fasciocutaneous flaps in the reconstruction of defects of the weight-bearing heel.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2003 Apr;13(4):216-8. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2003. PMID: 12718778
-
Comparative study of two series of distally based fasciocutaneous flaps for coverage of the lower one-fourth of the leg, the ankle, and the foot.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001 Feb;107(2):383-92. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200102000-00013. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001. PMID: 11214053
-
[Treatment of spoke heel injuries in children].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Oct;23(10):1180-2. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19957834 Chinese.
-
Effectiveness of the Reverse Sural Flap in Covering Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2022 Nov;30(4):368-377. doi: 10.1177/22925503211019617. Epub 2021 May 27. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2022. PMID: 36212103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The reverse sural artery flap for the reconstruction of distal third of the leg and foot.Int Wound J. 2014 Apr;11(2):210-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01075.x. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Int Wound J. 2014. PMID: 23050798 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of a reverse sural flap for posterior ankle soft-tissue defect following an injury in a patient from Tanzania.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021 Nov 23;9:2050313X211060685. doi: 10.1177/2050313X211060685. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34888053 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of modified reverse sural neurocutaneous flap repair on wound healing in patients with soft tissue defects of the foot and ankle.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jan 16;20(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05370-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39815356 Free PMC article.
-
Sural nerve preservation in reverse sural artery fasciocutaneous flap-a case report.Ann Surg Innov Res. 2012 Oct 9;6(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1750-1164-6-10. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2012. PMID: 23046550 Free PMC article.
-
[The one- and two-stage distally pedicled sural flap : surgical technique and clinical results].Unfallchirurg. 2012 Nov;115(11):988-93. doi: 10.1007/s00113-011-1952-7. Unfallchirurg. 2012. PMID: 21503802 Clinical Trial. German.
References
-
- Hsieh CH, Liang CC, Kueh NS, Tsai HH, Jeng SF. Distally based sural island flap for the reconstruction of a large soft tissue defect in an open tibial fracture with occluded anterior and posterior tibial arteries-a case report. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:112–115. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakajima H, Imanishi N, Fukuzumi S, Minabe T, Fukui Y, Miyasaka T, Kodama T, Aiso S, Fujino T. Accompanying arteries of the lesser saphenous vein and sural nerve: anatomic study and its clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;103:104–120. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199901000-00018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

