Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury
- PMID: 18423196
- PMCID: PMC7112336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.043
Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury
Abstract
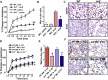
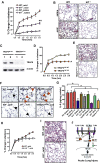
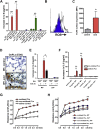
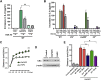
Multiple lung pathogens such as chemical agents, H5N1 avian flu, or SARS cause high lethality due to acute respiratory distress syndrome. Here we report that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) mutant mice display natural resistance to acid-induced acute lung injury (ALI). We show that TLR4-TRIF-TRAF6 signaling is a key disease pathway that controls the severity of ALI. The oxidized phospholipid (OxPL) OxPAPC was identified to induce lung injury and cytokine production by lung macrophages via TLR4-TRIF. We observed OxPL production in the lungs of humans and animals infected with SARS, Anthrax, or H5N1. Pulmonary challenge with an inactivated H5N1 avian influenza virus rapidly induces ALI and OxPL formation in mice. Loss of TLR4 or TRIF expression protects mice from H5N1-induced ALI. Moreover, deletion of ncf1, which controls ROS production, improves the severity of H5N1-mediated ALI. Our data identify oxidative stress and innate immunity as key lung injury pathways that control the severity of ALI.
Figures
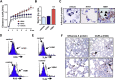
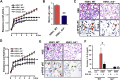
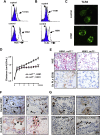
Comment in
-
A TRIFfic perspective on acute lung injury.Cell. 2008 Apr 18;133(2):208-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.006. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18423191 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of TLR4 does not prevent influenza A-induced mortality.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 May 15;189(10):1280-1. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201401-0193LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24832747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adachi O., Kawai T., Takeda K., Matsumoto M., Tsutsui H., Sakagami M., Nakanishi K., Akira S. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity. 1998;9:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Uematsu S., Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T.C., Da Silva K.A., Lewis J.F., Rodriguez-Capote K., Possmayer F., Veldhuizen R.A. Physiological and inflammatory response to instillation of an oxidized surfactant in a rat model of surfactant deficiency. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004;96:1674–1680. - PubMed
-
- Beigel J.H., Farrar J., Han A.M., Hayden F.G., Hyer R., de Jong M.D., Lochindarat S., Nguyen T.K., Nguyen T.H., Tran T.H., et al. Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1374–1385. - PubMed
-
- Binder C.J., Chang M.K., Shaw P.X., Miller Y.I., Hartvigsen K., Dewan A., Witztum J.L. Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002;8:1218–1226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

