Meiosis I is established through division-specific translational control of a cyclin
- PMID: 18423199
- PMCID: PMC2396536
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.032
Meiosis I is established through division-specific translational control of a cyclin
Abstract
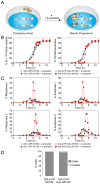
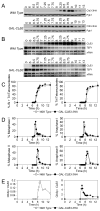
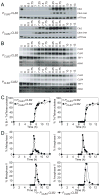
In budding yeast, key meiotic events such as DNA replication, recombination, and the meiotic divisions are controlled by Clb cyclin-dependent kinases (Clb-CDKs). Using a novel synchronization procedure, we have characterized the activity of these Clb-CDKs and observed a surprising diversity in their regulation during the meiotic divisions. Clb1-CDK activity is restricted to meiosis I, and Clb3-CDK activity to meiosis II, through 5'UTR-mediated translational control of its transcript. The analysis of cells inappropriately producing Clb3-CDKs during meiosis I furthermore defines Clb3 as an inhibitor of the meiosis I chromosome segregation program. Our results demonstrate an essential role for Clb-CDK regulation in establishing the meiotic chromosome segregation pattern.
Figures




References
-
- Bloom J, Cross FR. Multiple levels of cyclin specificity in cell-cycle control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:149–160. - PubMed
-
- Buonomo SB, Rabitsch KP, Fuchs J, Gruber S, Sullivan M, Uhlmann F, Petronczki M, Tóth A, Nasmyth K. Division of the nucleolus and its release of CDC14 during anaphase of meiosis I depends on separase, SPO12, and SLK19. Dev Cell. 2003;4:727–739. - PubMed
-
- Chu S, DeRisi J, Eisen M, Mulholland J, Botstein D, Brown PO, Herskowitz I. The transcriptional program of sporulation in budding yeast. Science. 1998;282:699–705. - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Fix O, Peters JM, Kirschner MW, Koshland D. Anaphase initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by the APC-dependent degradation of the anaphase inhibitor Pds1p. Genes Dev. 1996;10:3081–3093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

