Assessment of DNA double-strand breaks and gammaH2AX induced by the topoisomerase II poisons etoposide and mitoxantrone
- PMID: 18423498
- PMCID: PMC2581813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.03.005
Assessment of DNA double-strand breaks and gammaH2AX induced by the topoisomerase II poisons etoposide and mitoxantrone
Abstract
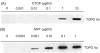
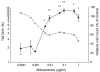
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) are highly deleterious DNA lesions as they lead to chromosome aberrations and/or apoptosis. The formation of nuclear DSBs triggers phosphorylation of histone H2AX on Ser-139 (defined as gammaH2AX), which participates in the repair of such DNA damage. Our aim was to compare the induction of gammaH2AX in relation to DSBs induced by topoisomerase II (TOPO II) poisons, etoposide (ETOP) and mitoxantrone (MXT), in V79 cells. DSBs were measured by the neutral comet assay, while gammaH2AX was quantified using immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry. Stabilized cleavage complexes (SCCs), lesions thought to be responsible for TOPO II poison-induced genotoxicity, were measured using a complex of enzyme-DNA assay. In the case of ETOP, a no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) and lowest observed effect level (LOEL) for genotoxicity was determined; gammaH2AX levels paralleled DSBs at all concentrations but significant DNA damage was not detected below 0.5 microg/ml. Furthermore, DNA damage was dependent on the formation of SCCs. In contrast, at low MXT concentrations (0.0001-0.001 microg/ml), induction of gammaH2AX was not accompanied by increases in DSBs. Rather, DSBs were only significantly increased when SCCs were detected. These findings suggest MXT-induced genotoxicity occurred via at least two mechanisms, possibly related to DNA intercalation and/or redox cycling as well as TOPO II inhibition. Our findings also indicate that gammaH2AX can be induced by DNA lesions other than DSBs. In conclusion, gammaH2AX, when measured using immunocytochemical and flow cytometric methods, is a sensitive indicator of DNA damage and may be a useful tool in genetic toxicology screens. ETOP data are consistent with the threshold concept for TOPO II poison-induced genotoxicity and this should be considered in the safety assessment of chemicals displaying an affinity for TOPO II and genotoxic/clastogenic effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of histone H2AX phosphorylation induced by DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibitors topotecan and mitoxantrone and by the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin.Cytometry A. 2004 Apr;58(2):99-110. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20018. Cytometry A. 2004. PMID: 15057963
-
Induction of ATM activation, histone H2AX phosphorylation and apoptosis by etoposide: relation to cell cycle phase.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 1;6(3):371-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.3.3835. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17297310
-
Relationship of DNA damage signaling to DNA replication following treatment with DNA topoisomerase inhibitors camptothecin/topotecan, mitoxantrone, or etoposide.Cytometry A. 2012 Jan;81(1):45-51. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.21172. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Cytometry A. 2012. PMID: 22140093 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity of topoisomerase II inhibitors: an anti-infective perspective.Toxicology. 2008 Dec 30;254(3):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.08.023. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18840496 Review.
-
Cytometry of ATM activation and histone H2AX phosphorylation to estimate extent of DNA damage induced by exogenous agents.Cytometry A. 2007 Sep;71(9):648-61. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20426. Cytometry A. 2007. PMID: 17622968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to b-LED Light While Exerting Antimicrobial Activity on Gram-Negative and -Positive Bacteria Promotes Transient EMT-like Changes and Growth Arrest in Keratinocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1896. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031896. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163819 Free PMC article.
-
A dual-activation, adenoviral-based system for the controlled induction of DNA double-strand breaks by the restriction endonuclease SacI.Biotechniques. 2009 Oct;47(4):847-54. doi: 10.2144/000113237. Biotechniques. 2009. PMID: 19852768 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage signaling assessed in individual cells in relation to the cell cycle phase and induction of apoptosis.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2012 Sep-Dec;49(5-6):199-217. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2012.738808. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2012. PMID: 23137030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damaging agents and p53 do not cause senescence in quiescent cells, while consecutive re-activation of mTOR is associated with conversion to senescence.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Dec;2(12):924-35. doi: 10.18632/aging.100265. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 21212465 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of the redox activity of ape1/ref-1 by e3330 blocks tnf-α-induced activation of IL-8 production in liver cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e70909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070909. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mills KD, Ferguson DO, Alt FW. The role of DNA breaks in genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2003;194:77–95. - PubMed
-
- Olive PL, Banath JP. Detection of DNA double-strand breaks through the cell cycle after exposure to X-rays, bleomycin, etoposide and 125IdUrd. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1993;64:349–358. - PubMed
-
- Kurose A, Tanaka T, Huang X, Halicka HD, Traganos F, Dai W, Darzynkiewicz Z. Assessment of ATM phosphorylation on Ser-1981 induced by DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibitors in relation to Ser-139-histone H2AX phosphorylation, cell cycle phase, and apoptosis. Cytometry A. 2005;68:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Ayene IS, Koch CJ, Krisch RE. DNA strand breakage by bivalent metal ions and ionizing radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007;83:195–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

