Combinatorial and rational approaches to polymer synthesis for medicine
- PMID: 18423930
- PMCID: PMC2536566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.02.005
Combinatorial and rational approaches to polymer synthesis for medicine
Abstract
High-throughput, combinatorial methods have revolutionized small molecule synthesis and drug discovery. By combining automation, miniaturization, and parallel synthesis techniques, large collections of new compounds have been synthesized and screened. It is becoming increasingly clear that these same approaches can also assist the discovery and development of novel biomaterials for medicine. This review examines combinatorial and rational polymer synthesis for medical applications, including stem cell engineering and nucleic acid drug delivery.
Figures

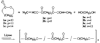


Similar articles
-
High-throughput and combinatorial technologies for tissue engineering applications.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2009 Sep;15(3):225-39. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2009.0049. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2009. PMID: 19290801 Review.
-
Combinatorial approaches in post-polymerization modification for rational development of therapeutic delivery systems.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jun;73:21-37. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29654990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in microwave-assisted combinatorial chemistry without polymer-supported reagents.Mol Divers. 2006 Aug;10(3):435-62. doi: 10.1007/s11030-006-9021-9. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Mol Divers. 2006. PMID: 16896542 Review.
-
Application of combinatorial and parallel synthesis chemistry methodologies to antiparasitic drug discovery.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Oct;11(19):2519-33. doi: 10.2174/0929867043364469. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15544460 Review.
-
Combinatorial and high-throughput screening of materials libraries: review of state of the art.ACS Comb Sci. 2011 Nov 14;13(6):579-633. doi: 10.1021/co200007w. Epub 2011 Aug 31. ACS Comb Sci. 2011. PMID: 21644562 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular design and evaluation of biodegradable polymers using a statistical approach.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013 Nov;24(11):2529-35. doi: 10.1007/s10856-013-5008-0. Epub 2013 Jul 26. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013. PMID: 23888354 Free PMC article.
-
An Oxygen-Tolerant PET-RAFT Polymerization for Screening Structure-Activity Relationships.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Feb 5;57(6):1557-1562. doi: 10.1002/anie.201711044. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29316089 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of osteoconductive and biodegradable polymers from a combinatorial polymer library.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010 May;93(2):807-16. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32769. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010. PMID: 20198696 Free PMC article.
-
Stiffness can mediate balance between hydrodynamic forces and avidity to impact the targeting of flexible polymeric nanoparticles in flow.Nanoscale. 2019 Apr 4;11(14):6916-6928. doi: 10.1039/c8nr09594a. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 30912772 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer design via SHAP and Bayesian machine learning optimizes pDNA and CRISPR ribonucleoprotein delivery.Chem Sci. 2024 Apr 22;15(19):7219-7228. doi: 10.1039/d3sc06920f. eCollection 2024 May 15. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38756796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langer R, Vacanti J. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110):920–926. - PubMed
-
- Langer R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature. 1998;392(6679 Supplement):5–10. - PubMed
-
- Brocchini S, et al. A combinatorial approach for polymer design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119(19):4553–4554.
-
- Brocchini S. Combinatorial chemistry and biomedical polymer development. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2001;53(1):123–130. - PubMed
-
- Ramstrom O, Lehn J-M. Drug discovery by dynamic combinatorial libraries. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2002;1(1):26–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

