NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activation in lung carcinoma cells by farnesol involves p65/RelA(Ser276) phosphorylation via the MEK-MSK1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 18424438
- PMCID: PMC2423266
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M800945200
NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activation in lung carcinoma cells by farnesol involves p65/RelA(Ser276) phosphorylation via the MEK-MSK1 signaling pathway
Abstract
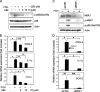
In this study, we demonstrate that treatment of human lung adenocarcinoma H460 cells with farnesol induces the expression of a number of immune response and inflammatory genes, including IL-6, CXCL3, IL-1alpha, and COX-2. This response was dependent on the activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Farnesol treatment reduces the level of IkappaBalpha and induces translocation of p65/RelA to the nucleus, its phosphorylation at Ser(276), and transactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Moreover, overexpression of IkappaBalpha or treatment with the NF-kappaB inhibitor caffeic acid phenethyl ester greatly diminishes the induction of inflammatory gene expression by farnesol. We provide evidence indicating that the farnesol-induced phosphorylation of p65/RelA at Ser(276) is important for optimal transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB. The MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 and knockdown of MEK1/2 expression with small interfering RNAs effectively blocked the phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)) but not that of Ser(536), suggesting that this phosphorylation is dependent on the activation of the MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway. We further show that inhibition of MSK1, a kinase acting downstream of MEK1/2-ERK1/2, by H89 or knockdown of MSK1 expression also inhibited phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)), suggesting that this phosphorylation is dependent on MSK1. Knockdown of MEK1/2 or MSK1 expression inhibits farnesol-induced expression of CXCL3, IL-1alpha, and COX-2 mRNA. Our results indicate that the induction of inflammatory genes by farnesol is mediated by the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and involves MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MSK1-dependent phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)). The activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by farnesol might be part of a prosurvival response during farnesol-induced ER stress.
Figures

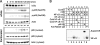

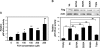

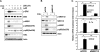
References
-
- Goldstein, J. L., and Brown, M. S. (1990) Nature 343 425–430 - PubMed
-
- Edwards, P. A., and Ericsson, J. (1999) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68 157–185 - PubMed
-
- Endres, M., and Laufs, U. (2004) Stroke 35 2708–2711 - PubMed
-
- Hanley, K., Komuves, L. G., Ng, D. C., Schoonjans, K., He, S. S., Lau, P., Bikle, D. D., Williams, M. L., Elias, P. M., Auwerx, J., and Feingold, K. R. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 11484–11491 - PubMed
-
- Rioja, A., Pizzey, A. R., Marson, C. M., and Thomas, N. S. (2000) FEBS Lett. 467 291–295 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

