Glucosamine found as a substituent of both phosphate groups in Bordetella lipid A backbones: role of a BvgAS-activated ArnT ortholog
- PMID: 18424515
- PMCID: PMC2446747
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01875-07
Glucosamine found as a substituent of both phosphate groups in Bordetella lipid A backbones: role of a BvgAS-activated ArnT ortholog
Abstract
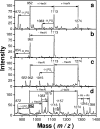
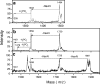
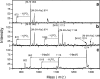
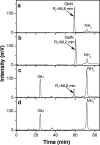
Endotoxins are amphipathic lipopolysaccharides (LPSs), major constituents of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. They consist of a lipid region, covalently linked to a core oligosaccharide, to which may be linked a repetitive glycosidic chain carrying antigenic determinants. Most of the biological activities of endotoxins have been associated with the lipid moiety of the molecule: unique to gram-negative bacteria, LPS is a ligand of the mammalian TLR4-MD2-CD14 pathogen recognition receptor complex. Lipid A preparations are often heterogeneous with respect to both the numbers and the lengths of fatty acids and the natures of substituents on the phosphate groups when present. The variants can significantly affect host immune responses. Nine species in the Bordetella genus have been described, and the fine LPS structures of seven of them have been published. In this report, lipids A from Bordetella pertussis Tohama I and B. bronchiseptica strain 4650 were further characterized and revealed to have a glucosamine substituting both lipid A phosphate groups of the diglucosamine backbone. These substitutions have not been previously described for bordetellae. Moreover, a B. pertussis transposon mutation that maps within a gene encoding a Bordetella ArnT (formerly PmrK) glycosyl transferase ortholog does not carry this substitution, thus providing a genetic basis for the modification. Reverse transcriptase PCR of this locus showed that it is Bvg regulated, suggesting that the ability of Bordetella to modify lipid A via this glucosamine modification is a potential virulence trait.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica Glycosyltransferase Core Mutants Trigger Changes in Lipid A Structure.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019 Sep;30(9):1679-1689. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02233-3. Epub 2019 Jun 12. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 31190311
-
Structure of the lipid A of Bordetella hinzii ATCC 51730.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2000;14(7):595-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(20000415)14:7<595::AID-RCM919>3.0.CO;2-4. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2000. PMID: 10775094
-
Complete Bordetella avium, Bordetella hinzii and Bordetella trematum lipid A structures and genomic sequence analyses of the loci involved in their modifications.Innate Immun. 2014 Aug;20(6):659-72. doi: 10.1177/1753425913506950. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 24127384
-
Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:295-329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.010307.145803. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17362200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental sensing mechanisms in Bordetella.Adv Microb Physiol. 2001;44:141-81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(01)44013-6. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11407112 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Peptide Resistance Genes in the Plant Pathogen Dickeya dadantii.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Oct 14;82(21):6423-6430. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01757-16. Print 2016 Nov 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27565623 Free PMC article.
-
Outer-Membrane-Vesicle-Associated O Antigen, a Crucial Component for Protecting Against Bordetella parapertussis Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 29;9:2501. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02501. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30459769 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the Bordetella LPS structural features that influence TLR4 downstream signaling.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1540534. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1540534. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40071202 Free PMC article.
-
Function and Biogenesis of Lipopolysaccharides.EcoSal Plus. 2018 Aug;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2018. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2018. EcoSal Plus. 2018. PMID: 30066669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural characterization of Bordetella parapertussis lipid A.J Lipid Res. 2009 May;50(5):854-9. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800454-JLR200. Epub 2008 Nov 17. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19017615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AFMB-CNRS. 9 February 2007, posting date. CAZy—carbohydrate-active enzymes. AFMB-CNRS, Universités Aix-Marseille I and II, Marseille, France. http://afmb.cnrs-mrs.fr/CAZY/.
-
- Allison, G. E., and N. K. Verma. 2000. Serotype-converting bacteriophages and O-antigen modification in Shigella flexneri. Trends Microbiol. 817-23. - PubMed
-
- Auger, G., J. van Heijenoort, D. Mengin-Lecreulx, and D. Blanot. 2003. A MurG assay which utilises a synthetic analogue of lipid I. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 219115-119. - PubMed
-
- Aussel, L., J. R. Brisson, M. B. Perry, and M. Caroff. 2000. Structure of the lipid A of Bordetella hinzii ATCC 51730. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 14595-599. - PubMed
-
- Aussel, L., R. Chaby, K. Le Blay, J. Kelly, P. Thibault, M. B. Perry, and M. Caroff. 2000. Chemical and serological characterization of the Bordetella hinzii lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 48540-46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

