Formate acts as a diffusible signal to induce Salmonella invasion
- PMID: 18424519
- PMCID: PMC2446767
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00205-08
Formate acts as a diffusible signal to induce Salmonella invasion
Abstract
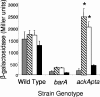
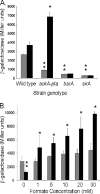
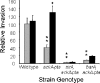
To infect an animal host, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium must penetrate the intestinal epithelial barrier. This process of invasion requires a type III secretion system encoded within Salmonella pathogenicity island I (SPI1). We found that a mutant with deletions of the acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase genes (ackA-pta) was deficient in invasion and SPI1 expression but that invasion gene expression was completely restored by supplying medium conditioned by growth of the wild-type strain, suggesting that a signal produced by the wild type, but not by the ackA-pta mutant, was required for invasion. This mutant also excreted 68-fold-less formate into the culture medium, and the addition of sodium formate to cultures restored both the expression of SPI1 and the invasion of cultured epithelial cells by the mutant. The effect of formate was pH dependent, requiring a pH below neutrality, and studies in mice showed that the distal ileum, the preferred site of Salmonella invasion in this species, had the appropriate formate concentration and pH to elicit invasion, while the cecum contained no detectable formate. Furthermore, we found that formate affected the major regulators of SPI1, hilA and hilD, but that the primary routes of formate metabolism played no role in its activity as a signal.
Figures



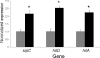
Similar articles
-
Intestinal Long-Chain Fatty Acids Act as a Direct Signal To Modulate Expression of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System.mBio. 2016 Feb 16;7(1):e02170-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02170-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 26884427 Free PMC article.
-
Signal pathway in salt-activated expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jul;190(13):4624-31. doi: 10.1128/JB.01957-07. Epub 2008 Apr 25. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18441068 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) and SPI4 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2008 Mar;76(3):1024-35. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01224-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18160484 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
-
The Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 type III secretion system.Microbes Infect. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(14-15):1281-91. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01488-5. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11755416 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of diet on pathogen performance in the microbiome.Microbiome Res Rep. 2022 Mar 26;1(2):13. doi: 10.20517/mrr.2021.10. eCollection 2022. Microbiome Res Rep. 2022. PMID: 38045644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging insights on intestinal dysbiosis during bacterial infections.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Feb;17(100):67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 29. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24581695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molybdenum Enzymes and How They Support Virulence in Pathogenic Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 11;11:615860. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.615860. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33362753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diffusible Signal Factors Act through AraC-Type Transcriptional Regulators as Chemical Cues To Repress Virulence of Enteric Pathogens.Infect Immun. 2020 Sep 18;88(10):e00226-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00226-20. Print 2020 Sep 18. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32690633 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of bacterial virulence by Csr (Rsm) systems.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015 Jun;79(2):193-224. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00052-14. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25833324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmer, B. M., J. van Reeuwijk, P. R. Watson, T. S. Wallis, and F. Heffron. 1999. Salmonella SirA is a global regulator of genes mediating enteropathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 31971-982. - PubMed
-
- Altier, C., M. Suyemoto, A. I. Ruiz, K. D. Burnham, and R. Maurer. 2000. Characterization of two novel regulatory genes affecting Salmonella invasion gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 35635-646. - PubMed
-
- Argenzio, R. A., and M. Southworth. 1975. Sites of organic acid production and absorption in gastrointestinal tract of the pig. Am. J. Physiol. 228454-460. - PubMed
-
- Argenzio, R. A., M. Southworth, and C. E. Stevens. 1974. Sites of organic acid production and absorption in the equine gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. 2261043-1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

