The ArgP protein stimulates the Klebsiella pneumoniae gdhA promoter in a lysine-sensitive manner
- PMID: 18424527
- PMCID: PMC2446773
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00295-08
The ArgP protein stimulates the Klebsiella pneumoniae gdhA promoter in a lysine-sensitive manner
Abstract
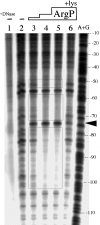
The lysine-sensitive factor that binds to the upstream region of the Klebsiella pneumoniae gdhA promoter and stimulates gdhA transcription during growth in minimal medium has been proposed to be the K. pneumoniae ArgP protein (M. R. Nandineni, R. S. Laishram, and J. Gowrishankar, J. Bacteriol. 186:6391-6399, 2004). A knockout mutation of the K. pneumoniae argP gene was generated and used to assess the roles of exogenous lysine and argP in the regulation of the gdhA promoter. Disruption of argP reduced the strength and the lysine-dependent regulation of the gdhA promoter. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays using crude extracts prepared from wild-type and argP-defective strains indicted the presence of an argP-dependent factor whose ability to bind the gdhA promoter was lysine sensitive. DNase I footprinting studies using purified K. pneumoniae ArgP protein indicated that ArgP bound the region that lies approximately 50 to 100 base pairs upstream of the gdhA transcription start site in a manner that was sensitive to the presence of lysine. Substitutions within the region bound by ArgP affected the binding of ArgP to the gdhA promoter region in vitro and the argP-dependent stimulation of the gdhA promoter in vivo. These observations suggest that elevated intracellular levels of lysine reduce the affinity of ArgP for its binding site at the gdhA promoter, preventing ArgP from binding to and stimulating transcription from the promoter in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of ArgP (IciA) in lysine-mediated repression in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2011 Nov;193(21):5985-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.05869-11. Epub 2011 Sep 2. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21890697 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of tetramer formation by the nitrogen assimilation control protein for strong repression of glutamate dehydrogenase formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2005 Dec;187(24):8291-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.24.8291-8299.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16321933 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ArgP and Lrp as transcriptional regulators of lysP, the gene encoding the specific lysine permease of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2011 May;193(10):2536-48. doi: 10.1128/JB.00815-10. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21441513 Free PMC article.
-
Differential protein-DNA contacts for activation and repression by ArgP, a LysR-type (LTTR) transcriptional regulator in Escherichia coli.Microbiol Res. 2018 Jan;206:141-158. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 29146251
-
Lysine represses transcription of the Escherichia coli dapB gene by preventing its activation by the ArgP activator.J Bacteriol. 2008 Aug;190(15):5224-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01782-07. Epub 2008 May 23. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18502871 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic analysis of the nitrogen assimilation control protein from Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4834-46. doi: 10.1128/JB.01114-09. Epub 2010 Aug 6. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20693327 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ArgP (IciA) in lysine-mediated repression in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2011 Nov;193(21):5985-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.05869-11. Epub 2011 Sep 2. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21890697 Free PMC article.
-
A NAC for regulating metabolism: the nitrogen assimilation control protein (NAC) from Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4801-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.00266-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20675498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of the NAC (nitrogen assimilation control protein)-binding site within the ureD promoter of Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4821-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.00883-09. Epub 2010 Jul 9. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20622063 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen assimilation in Escherichia coli: putting molecular data into a systems perspective.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013 Dec;77(4):628-95. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00025-13. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24296575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenchley, J. E., M. J. Prival, and B. Magasanik. 1973. Regulation of the synthesis of enzymes responsible for glutamate formation in Klebsiella aerogenes. J. Biol. Chem. 2486122-6128. - PubMed
-
- Charlier D., and N. Glansdorff. September 2004, posting date. Chapter 3.6.1.10, Biosynthesis of arginine and polyamines. In R. Curtiss III et al. (ed.), EcoSal-Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. ASM Press, Washington, DC. http://www.ecosal.org. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

