Rapid screening of quorum-sensing signal N-acyl homoserine lactones by an in vitro cell-free assay
- PMID: 18424536
- PMCID: PMC2446546
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02869-07
Rapid screening of quorum-sensing signal N-acyl homoserine lactones by an in vitro cell-free assay
Abstract
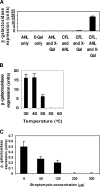
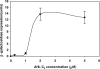
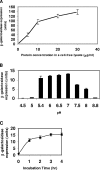
A simple, sensitive, and rapid cell-free assay system was developed for detection of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) autoinducers involved in bacterial quorum sensing (QS). The present approach improves upon previous whole-cell biosensor-based approaches in its utilization of a cell-free assay approach to conduct bioassays. The cell-free assay was derived from the AHL biosensor bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens NTL4(pCF218)(pCF372), allowing the expression of beta-galactosidase upon addition of exogenous AHLs. We have shown that beta-galactosidase expression is possible in cell-free solution [lysate from Agrobacterium tumefaciens NTL4(pCF218)(pCF372) culture]. Assay detection limits with the use of chromogenic substrate X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside) ranged from approximately 100 nM to 300 nM depending on the specific AHL. Replacement (of X-Gal) with the luminescent substrate Beta-Glo increased sensitivity to AHLs by 10-fold. A major advantage of the cell-free assay system is elimination of time-consuming steps for biosensor cell culture conditioning, which are required prior to whole-cell bioassays. This significantly reduced assay times from greater than 24 h to less than 3 h, while maintaining high sensitivity. Assay lysate may be prepared in bulk and stored (-80 degrees C) over 6 months for future use. Finally, the present protocol may be adapted for use with other biosensor strains and be used in high-throughput AHL screening of bacteria or metagenomic libraries.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrochemical detection of quorum sensing signaling molecules by dual signal confirmation at microelectrode arrays.Anal Chem. 2011 Mar 15;83(6):2097-103. doi: 10.1021/ac1028243. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21323339
-
Detection of N-acyl homoserine lactones using a traI-luxCDABE-based biosensor as a high-throughput screening tool.BMC Biotechnol. 2008 Jul 30;8:59. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-59. BMC Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18667064 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive whole-cell biosensor suitable for detecting a variety of N-acyl homoserine lactones in intact rhizosphere microbial communities.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jun;73(11):3724-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02187-06. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17400771 Free PMC article.
-
Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing by enzymatic disruption of signal molecules.Acta Biochim Pol. 2009;56(1):1-16. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2009. PMID: 19287806 Review.
-
Beneficial effects of bacteria-plant communication based on quorum sensing molecules of the N-acyl homoserine lactone group.Plant Mol Biol. 2016 Apr;90(6):605-12. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0457-8. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Plant Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26898296 Review.
Cited by
-
AHLs-produced bacteria in refrigerated shrimp enhanced the growth and spoilage ability of Shewanella baltica.J Food Sci Technol. 2019 Jan;56(1):114-121. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3464-8. Epub 2018 Nov 8. J Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 30728552 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of quorum sensing genes in biofilm development and PAHs degradation by a marine bacterium.Bioengineered. 2016 Apr;7(3):205-11. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2016.1174797. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Bioengineered. 2016. PMID: 27111260 Free PMC article.
-
Circular single-stranded DNA as a programmable vector for gene regulation in cell-free protein expression systems.Nat Commun. 2024 May 31;15(1):4635. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49021-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38821953 Free PMC article.
-
Photoluminescence-Based Bioassay With Cysteamine-Capped TiO2 Nanoparticles for the Selective Recognition of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactones.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 3;9:750933. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.750933. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34926417 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing and the Use of Quorum Quenchers as Natural Biocides to Inhibit Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2016 Dec 15;5(4):39. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics5040039. Antibiotics (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27983678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassler, B. L. 2002. Small talk: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Cell 109:421-424. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantity of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brock, T. D. 1964. Action of streptomycin and related antibiotics. Fed. Proc. 23:965-975. - PubMed
-
- Camara, M., P. Williams, and A. Hardman. 2002. Controlling infection by tuning in and tuning down the volume of bacterial small-talk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2:667-676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

