Disruption of mutually negative regulatory feedback loop between interferon-inducible p202 protein and the E2F family of transcription factors in lupus-prone mice
- PMID: 18424712
- PMCID: PMC2810195
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.5927
Disruption of mutually negative regulatory feedback loop between interferon-inducible p202 protein and the E2F family of transcription factors in lupus-prone mice
Abstract
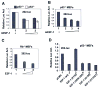
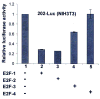
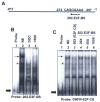
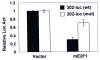
Studies have identified IFN-inducible Ifi202 gene as a lupus susceptibility gene (encoding p202 protein) in mouse models of lupus disease. However, signaling pathways that regulate the Ifi202 expression in cells remain to be elucidated. We found that steady-state levels of Ifi202 mRNA and protein were high in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from E2F1 knockout (E2F1(-/-)) and E2F1 and E2F2 double knockout (E2F1(-/-)E2F2(-/-)) mice than isogenic wild-type MEFs. Moreover, overexpression of E2F1 in mouse fibroblasts decreased expression of p202. Furthermore, expression of E2F1, but not E2F4, transcription factor in mouse fibroblasts repressed the activity of 202-luc-reporter in promoter-reporter assays. Interestingly, the E2F1-mediated transcriptional repression of the 202-luc-reporter was independent of p53 and pRb expression. However, the repression was dependent on the ability of E2F1 to bind DNA. We have identified a potential E2F DNA-binding site in the 5'-regulatory region of the Ifi202 gene, and mutations in this E2F DNA-binding site reduced the E2F1-mediated transcriptional repression of 202-luc-reporter. Because p202 inhibits the E2F1-mediated transcriptional activation of genes, we compared the expression of E2F1 and its target genes in splenic cells from lupus-prone B6.Nba2 congenic mice, which express increased levels of p202, with age-matched C57BL/6 mice. We found that increased expression of Ifi202 in the congenic mice was associated with inhibition of E2F1-mediated transcription and decreased expression of E2F1 and its target genes that encode proapoptotic proteins. Our observations support the idea that increased Ifi202 expression in certain strains of mice contributes to lupus susceptibility in part by inhibiting E2F1-mediated functions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased expression of Ifi202, an IFN-activatable gene, in B6.Nba2 lupus susceptible mice inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis.J Immunol. 2006 May 15;176(10):5863-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.5863. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16670293
-
Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein upregulates expression of the Ifi202 gene encoding an interferon-inducible negative regulator of cell growth.Oncogene. 2003 Jul 31;22(31):4775-85. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206780. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12894219
-
Aim2 deficiency stimulates the expression of IFN-inducible Ifi202, a lupus susceptibility murine gene within the Nba2 autoimmune susceptibility locus.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7385-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002468. Epub 2010 Nov 5. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21057088 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes in systemic lupus erythematosus.Immunol Lett. 2008 Aug 15;119(1-2):32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18598717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-inducible p202 in the susceptibility to systemic lupus.Front Biosci. 2002 May 1;7:e252-62. doi: 10.2741/A921. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11991834 Review.
Cited by
-
Absent in melanoma 2 proteins in the development of cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Dec;73(23):4383-4395. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2296-9. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27328971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes as modifiers of lupus susceptibility.Immunol Lett. 2012 Sep;147(1-2):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Immunol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22841963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for the interferon-inducible p200-family proteins in sex bias in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):893-906. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0073. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21902548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasomes in the pathophysiology of autoinflammatory syndromes.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Mar;107(3):379-391. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR0919-191R. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31608507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA-responsive inflammasomes and their regulators in autoimmunity.Clin Immunol. 2012 Mar;142(3):223-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2011.12.007. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22245264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–306. - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC, Kammer GM. Molecular aberrations in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Today. 2000;6:418–424. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferon (α/β) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–336. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen TN, Gubbels MR, Kotzin BL. New insights into disease pathogenesis from mouse lupus genetics. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Mohan C. SLE 1, 2, 3…genetic dissection of lupus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;601:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

