Novel preparation of graded porous structures for medical engineering
- PMID: 18426768
- PMCID: PMC2607349
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0092
Novel preparation of graded porous structures for medical engineering
Abstract
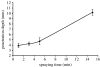
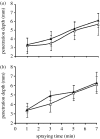
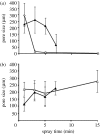
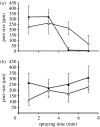
The gradation of porosity in a biomaterial can be very useful for a variety of medical engineering applications such as filtration, bone replacement and implant development. However, the preparation of such structures is not a technologically trivial task and replication methods do not offer an easy solution. In this work, we elucidate the preparation of structures having a graded porosity by electrohydrodynamic spraying, using zirconia (ZrO2), which is widely used in biomedical and other applications. The processes are generic and can be achieved using other bioactive ceramics with similar particle characteristics. The pores on the sprayed surface, the innermost surface and lengthwise cross sections have been analysed in addition to the change in depth of penetration as a function of spraying time. Control of porosity, pore size and depth of penetration has been obtained by varying parameters such as the spraying time, sintering temperature and the sacrificial template. It has been possible to obtain structures with interconnected pore networks of pore size greater than 100microm as well as scattered pores smaller than 10microm in size.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characteristics of hydroxyapatite coated titanium porous coatings on Ti-6Al-4V substrates by plasma sprayed method.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007 Aug;82(2):450-9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30750. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007. PMID: 17245748
-
Porous biomorphic silicon carbide ceramics coated with hydroxyapatite as prospective materials for bone implants.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Nov 1;68:143-152. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.05.113. Epub 2016 May 26. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27524006
-
Improvement of the microstructure and mechanical properties of bioceramic scaffolds using electrohydrodynamic spraying with template modification.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010 Apr;3(3):230-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Oct 14. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010. PMID: 20142107
-
Development of plasma-sprayed bioceramic coatings with bond coats based on titania and zirconia.Biomaterials. 1998 Aug;19(16):1507-11. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00067-2. Biomaterials. 1998. PMID: 9794527 Review.
-
Ceramics in orthopaedics.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000 Nov;82(8):1095-9. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.82b8.11744. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000. PMID: 11132264 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Geometry Design Optimization of Functionally Graded Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Mechanobiological Approach.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 15;11(1):e0146935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146935. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26771746 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate and Efficient Thermal Stress Analyses of Functionally Graded Solids Using Incompatible Graded Finite Elements.Compos Struct. 2019 Aug 15;222:110909. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.110909. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Compos Struct. 2019. PMID: 32189823 Free PMC article.
-
Graded porous β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in mandible augmentation.J Craniofac Surg. 2015 Mar;26(2):e148-53. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001383. J Craniofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25675019 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial and biological properties of the gradient coating on polyamide substrate for bone substitute.J R Soc Interface. 2014 Oct 6;11(99):20140101. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0101. J R Soc Interface. 2014. PMID: 25121648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castillo M, Moore J.J, Schowengerdt F.D, Ayers R.A, Zhang X, Umakoshi M, Yi H.C, Guigne J.Y. Effects of gravity on combustion synthesis of functionally graded biomaterials. Adv. Space Res. 2003;32:265–270. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(03)90261-4. - DOI
-
- Chen Q.Z, Boccaccini A.R, Zhang H.B, Wang D.Z, Edirisinghe M.J. Improved mechanical reliability of bone tissue engineering (zirconia) scaffolds by electrospraying. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006;89:1534–1539. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.00935.x. - DOI
-
- Christel P, Meunier A, Dorlot J.M, Crolet J.M, Witvolet J, Sedel L, Boutin P. Biomechanical compatibility and design of ceramic implants for orthopedic surgery. In: Ducheyne P, Lemons J, editors. Bioceramics: material characteristics versus in vivo behaviour. Annals of New York Academy of Sciences; New York, NY: 1988. pp. 234–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

