Caspase-2 cleavage of BID is a critical apoptotic signal downstream of endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 18426910
- PMCID: PMC2423129
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00013-08
Caspase-2 cleavage of BID is a critical apoptotic signal downstream of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
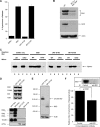
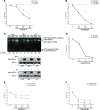
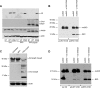
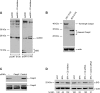
The accumulation of misfolded proteins stresses the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and triggers cell death through activation of the multidomain proapoptotic BCL-2 proteins BAX and BAK at the outer mitochondrial membrane. The signaling events that connect ER stress with the mitochondrial apoptotic machinery remain unclear, despite evidence that deregulation of this pathway contributes to cell loss in many human degenerative diseases. In order to "trap" and identify the apoptotic signals upstream of mitochondrial permeabilization, we challenged Bax-/- Bak-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts with pharmacological inducers of ER stress. We found that ER stress induces proteolytic activation of the BH3-only protein BID as a critical apoptotic switch. Moreover, we identified caspase-2 as the premitochondrial protease that cleaves BID in response to ER stress and showed that resistance to ER stress-induced apoptosis can be conferred by inhibiting caspase-2 activity. Our work defines a novel signaling pathway that couples the ER and mitochondria and establishes a principal apoptotic effector downstream of ER stress.
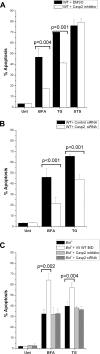
Figures
References
-
- Calfon, M., H. Zeng, F. Urano, J. H. Till, S. R. Hubbard, H. P. Harding, S. G. Clark, and D. Ron. 2002. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 41592-96. - PubMed
-
- Cheung, H. H., N. Lynn Kelly, P. Liston, and R. G. Korneluk. 2006. Involvement of caspase-2 and caspase-9 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: a role for the IAPs. Exp. Cell Res. 3122347-2357. - PubMed
-
- Chipuk, J. E., L. Bouchier-Hayes, and D. R. Green. 2006. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 131396-1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
