Collecting duct renin is upregulated in both kidneys of 2-kidney, 1-clip goldblatt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 18426992
- PMCID: PMC2601698
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.110916
Collecting duct renin is upregulated in both kidneys of 2-kidney, 1-clip goldblatt hypertensive rats
Abstract
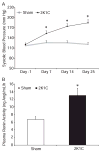
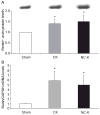
Renin in collecting duct cells is upregulated in chronic angiotensin II-infused rats via angiotensin II type 1 receptors. To determine whether stimulation of collecting duct renin is a blood pressure-dependent effect; changes in collecting duct renin and associated parameters were assessed in both kidneys of 2-kidney, 1-clip Goldblatt hypertensive (2K1C) rats. Renal medullary tissues were used to avoid the contribution of renin from juxtaglomerular cells. Systolic blood pressure increased to 184+/-9 mm Hg in 2K1C rats (n=19) compared with sham rats (121+/-6 mm Hg; n=12). Although renin immunoreactivity markedly decreased in juxtaglomerular cells of nonclipped kidneys (NCK: 0.2+/-0.0 versus 1.0+/-0.0 relative ratio) and was augmented in clipped kidneys (CK: 1.7+/-1.0 versus 1.0+/-0.0 relative ratio), its immunoreactivity increased in cortical and medullary collecting ducts of both kidneys of 2K1C rats (CK: 2.8+/-1.0 cortex; 2.1+/-1.0 medulla; NCK: 4.6+/-2.0 cortex, 3.2+/-1.0 medulla versus 1.0+/-0.0 in sham kidneys). Renal medullary tissues of 2K1C rats showed greater levels of renin protein (CK: 1.4+/-0.2; NCK: 1.5+/-0.3), renin mRNA (CK: 5.8+/-2.0; NCK: 4.9+/-2.0), angiotensin I (CK: 120+/-18 pg/g; NCK: 129+/-13 pg/g versus sham: 67+/-6 pg/g), angiotensin II (CK: 150+/-32 pg/g; NCK: 123+/-21 pg/g versus sham: 91+/-12 pg/g; P<0.05), and renin activity (CK: 8.6 microg of angiotensin I per microgram of protein; NCK: 8.3 microg of angiotensin I per microgram of protein; sham: 3.4 microg of angiotensin I per microgram of protein) than sham rats. These data indicate that enhanced collecting duct renin in 2K1C rats occurs independently of blood pressure. Upregulation of distal tubular renin helps to explain how sustained intrarenal angiotensin II formation occurs even during juxtaglomerular renin suppression, thus allowing maintained effects on tubular sodium reabsorption that contribute to the hypertension.
Figures
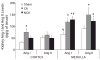
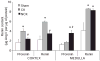

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal changes in renal ACE/ANG II and ACE2/ANG 1-7 are associated with enhanced collecting duct renin in Goldblatt hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):F749-55. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00383.2009. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21209009 Free PMC article.
-
AT1 receptor-mediated enhancement of collecting duct renin in angiotensin II-dependent hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Sep;289(3):F632-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00462.2004. Epub 2005 May 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15870381 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential activation of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in the progression of hypertensive nephropathy in Goldblatt rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):F195-206. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00001.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26823279
-
[The cortical collecting duct plays a pivotal role in the kidney's local renin-angiotensin system].Orv Hetil. 2013 Apr 28;154(17):643-9. doi: 10.1556/OH.2013.29597. Orv Hetil. 2013. PMID: 23608311 Review. Hungarian.
-
Intrarenal angiotensin II generation and renal effects of AT1 receptor blockade.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Apr;10 Suppl 12:S266-72. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10201881 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Angiotensin II Type 1A Receptor on ACE2, Neprilysin and KIM-1 in Two Kidney One Clip (2K1C) Model of Renovascular Hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 29;11:602985. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.602985. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33708117 Free PMC article.
-
The intrarenal generation of angiotensin II is required for experimental hypertension.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;21:73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25616034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Deletion of AT1a Receptor or Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Selectively in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney Attenuates Two-Kidney, One-Clip Goldblatt Hypertension in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15798. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415798. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555438 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of complement alternative pathway activation in hypertensive renal damage.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 May;247(9):797-804. doi: 10.1177/15353702221091986. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35473318 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of ENaC in collecting duct cells by prorenin and its receptor PRR: involvement of Nox4-derived hydrogen peroxide.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):F1243-50. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00492.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26697985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeNicola L, Keiser JA, Blantz RC, Gabbai FB. Angiotensin II and renal functional reserve in rats with Goldblatt hypertension. Hypertension. 1992;19:790–794. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell KD, Jacinto SM, Mullins JJ. Proximal tubular fluid, kidney, and plasma levels of angiotensin II in hypertensive ren-2 transgenic rats. Am J Physiol-Renal Physiol. 1997;273:F246–F253. - PubMed
-
- Zou L, Imig JD, Von Thun AM, Hymel A, Ono H, Navar LG. Receptor-mediated intrarenal ANG II augmentation in ANG II-infused rats. Hypertension. 1996;28:669–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

