Endosomal sorting complex required for transport proteins in cancer pathogenesis, vesicular transport, and non-endosomal functions
- PMID: 18429951
- PMCID: PMC11158640
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00825.x
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport proteins in cancer pathogenesis, vesicular transport, and non-endosomal functions
Abstract
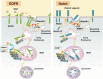
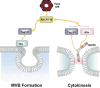
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) proteins form a multicomplex sorting machinery that controls multivesicular body (MVB) formation and the sorting of ubiquitinated membrane proteins to the endosomes. Being sorted to the MVB generally results in the lysosome-dependent degradation of cell-surface receptors, and defects in this machinery induce dysregulated receptor traffic and turnover. Recent lessons from gene targeting and silencing methodologies have implicated the ESCRT in normal development, cell differentiation, and growth, as well as in the budding of certain enveloped viruses. Furthermore, it is becoming apparent that the dysregulation of ESCRT proteins is involved in the development of various human diseases, including many types of cancers and neurodegenerative disorders. Here, we summarize the roles of ESCRT proteins in MVB sorting processes and the regulation of tumor cells, and we discuss some of their other functions that are unrelated to vesicular transport.
Figures

References
-
- Gruenberg J, Stenmark H. The biogenesis of multivesicular endosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 317–23. - PubMed
-
- Babst M. A protein's final ESCRT. Traffic 2005; 6: 2–9. - PubMed
-
- Luzio JP, Rous BA, Bright NA, Pryor PR, Mullock BM, Piper RC. Lysosome–endosome fusion and lysosome biogenesis. J Cell Sci 2000; 113: 1515–24. - PubMed
-
- Van Der Goot FG, Gruenberg J. Oiling the wheels of the endocytic pathway. Trends Cell Biol 2002; 12: 296–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

