FDG-PET imaging for the evaluation of antiglioma agents in a rat model
- PMID: 18430796
- PMCID: PMC2563051
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2008-014
FDG-PET imaging for the evaluation of antiglioma agents in a rat model
Abstract
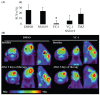
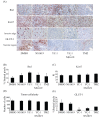
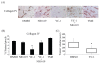
The increasing development of novel anticancer agents demands parallel advances in the methods used to rapidly assess their therapeutic efficacy (TE) in the preclinical phase. We evaluated the ability of small-animal PET, using the (18)F-fluoro-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) radiotracer, to predict the TE of a number of anticancer agents in the rat C6 glioma model following 3 days of treatment. Semi-quantitative measurements of changes in FDG uptake during the course of treatment (standardized uptake value response [SUV(r)]) were found to be significantly lower in tumors treated with the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha inhibitor YC-1 (15 mg/kg) than in tumors in the control group. No significant SUV(r) change was observed following a similar 3-day regimen with the proapoptotic agent NS1619 (20 microg/kg), the combination of YC-1 and NS1619, or the alkylating agent temozolomide (7.5 mg/kg). Quantitative immunohistochemical studies demonstrated significantly lower levels of glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1) expression in the YC-1-treated tumors, thereby correlating with the low SUV(r) observed in this group. The ability of SUV(r) to predict gold-standard outcomes of TE was further validated as YC-1-treated tumors had decreased volumes compared to control tumors. As such, we successfully demonstrated the ability of FDG-PET to rapidly determine the TE of novel agents for the treatment of glioma in the preclinical phase of evaluation.
Figures
References
-
- Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. Survey: new medicines in development for cancer. [Accessed May 17, 2005]. Available at http://www.phrma.org/files/Cancer%20Survey.pdf.
-
- Zijdenbos AP, Lerch JP, Bedell BJ, Evans AC. Brain imaging in drug R&D. Biomarkers. 2005;10(suppl 1):S58 – S68. - PubMed
-
- Knoess C, Siegel S, Smith A, et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET R4 PET scanner for rodents. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:737–747. - PubMed
-
- Kelloff GJ, Hoffman JM, Johnson B, et al. Progress and promise of FDG-PET imaging for cancer patient management and oncologic drug development. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2785 – 2808. - PubMed
-
- Aliaga A, Rousseau JA, Cadorette J, et al. A small animal positron emission tomography study of the effect of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy on the uptake of 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose in murine models of breast cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2007;9:144 – 150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

