Specificity of ADAR-mediated RNA editing in newly identified targets
- PMID: 18430892
- PMCID: PMC2390793
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.923308
Specificity of ADAR-mediated RNA editing in newly identified targets
Abstract
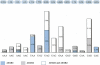
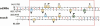
Adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADARs) convert adenosines to inosine in both coding and noncoding double-stranded RNA. Deficiency in either ADAR1 or ADAR2 in mice is incompatible with normal life and development. While the ADAR2 knockout phenotype can be attributed to the lack of editing of the GluR-B receptor, the embryonic lethal phenotype caused by ADAR1 deficiency still awaits clarification. Recently, massive editing was observed in noncoding regions of mRNAs in mice and humans. Moreover, editing was observed in protein-coding regions of four mRNAs encoding FlnA, CyFip2, Blcap, and IGFBP7. Here, we investigate which of the two active mammalian ADAR enzymes is responsible for editing of these RNAs and whether any of them could possibly contribute to the phenotype observed in ADAR knockout mice. Editing of Blcap, FlnA, and some sites within B1 and B2 SINEs clearly depends on ADAR1, while other sites depend on ADAR2. Based on our data, substrate specificities can be further defined for ADAR1 and ADAR2. Future studies on the biological implications associated with a changed editing status of the studied ADAR targets will tell whether one of them turns out to be directly or indirectly responsible for the severe phenotype caused by ADAR1 deficiency.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
