A cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE8B) that is mutated in adrenal hyperplasia is expressed widely in human and mouse tissues: a novel PDE8B isoform in human adrenal cortex
- PMID: 18431404
- PMCID: PMC2671148
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.85
A cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE8B) that is mutated in adrenal hyperplasia is expressed widely in human and mouse tissues: a novel PDE8B isoform in human adrenal cortex
Abstract
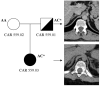
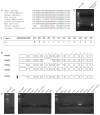
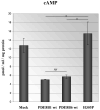
Bilateral adrenocortical hyperplasia (BAH) is the second most common cause of corticotropin-independent Cushing syndrome (CS). Genetic forms of BAH have been associated with complex syndromes such as Carney Complex and McCune-Albright syndrome or may present as isolated micronodular adrenocortical disease (iMAD) usually in children and young adults with CS. A genome-wide association study identified inactivating phosphodiesterase (PDE) 11A (PDE11A)-sequencing defects as low-penetrance predisposing factors for iMAD and related abnormalities; we also described a mutation (c.914A > C/H305P) in cyclic AMP (cAMP)-specific PDE8B, in a patient with iMAD. In this study we further characterize this mutation; we also found a novel PDE8B isoform that is highly expressed in the adrenal gland. This mutation is shown to significantly affect the ability of the protein to degrade cAMP in vitro. Tumor tissues from patients with iMAD and no mutations in the coding PDE8B sequence or any other related genes (PRKAR1A, PDE11A) showed downregulated PDE8B expression (compared to normal adrenal cortex). Pde8b is detectable in the adrenal gland of newborn mice and is widely expressed in other mouse tissues. We conclude that PDE8B is another PDE gene linked to iMAD; it is a candidate causative gene for other adrenocortical lesions linked to the cAMP signaling pathway and possibly for tumors in other tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Stratakis CA, Boikos SA. Genetics of adrenal tumors associated with Cushing’s syndrome: a new classification for bilateral adrenocortical hyperplasias. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:748–757. - PubMed
-
- Gunther DF, Bourdeau I, Matyakhina L, et al. Cyclical Cushing syndrome presenting in infancy: an early form of primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease, or a new entity? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:3173–3182. - PubMed
-
- Stratakis CA. Adrenocortical tumors, primary pigmented adrenocortical disease (PPNAD)/Carney complex, and other bilateral hyperplasias: the NIH studies. Horm Metab Res. 2007;39:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J. Endocrine manifestations o stimulatory G protein -subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:675–705. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner LS, Carney JA, Pack SD, et al. Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit in patients with the Carney complex. Nat Genet. 2000;26:89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

