Telemetric monitoring of 24 h intraocular pressure in conscious and freely moving C57BL/6J and CBA/CaJ mice
- PMID: 18431454
- PMCID: PMC2324118
Telemetric monitoring of 24 h intraocular pressure in conscious and freely moving C57BL/6J and CBA/CaJ mice
Abstract
Purpose: To study change patterns of 24 h intraocular pressure (IOP) in conscious and freely moving mice using telemetry.
Methods: Adult C57BL/6J and CBA/CaJ mice were entrained to a standard 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle. A telemetric pressure transmitter was implanted subcutaneously on the upper back of each light-dark entrained mouse, and the pressure catheter tip was inserted into the vitreous chamber. Broadcasted IOP data were received at 120 Hz. Means of 2 min IOP were recorded every 5 min for 4-13 days to generate the 24 h IOP pattern in each mouse strain. The pattern of IOP in the C57BL/6J strain was also determined under an acute constant dark condition for 24 h.
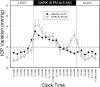
Results: There were distinct patterns of 24 h IOP in the C57BL/6J and CBA/CaJ mouse strains. Under the standard light-dark condition, IOP was higher during the dark period than the light period in both strains. Elevation in IOP from the light period to the dark period was significantly smaller in the CBA/CaJ strain (1.6+/-1.7 mmHg, mean+/- standard deviation (SD), n=21) than in the C57BL/6J strain (3.4+/-2.5 mmHg, n=20). The 24 h IOP pattern in the C57BL/6J strain persisted under an acute constant dark condition (n=8).
Conclusions: Distinct change patterns of 24 h IOP appeared in these two mouse strains. Although mean IOP during the dark period was significantly higher than the light period in both strains, the magnitudes of light-dark IOP elevation differed. The 24 h IOP change pattern can be driven endogenously in the absence of light.
Figures
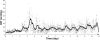

Similar articles
-
Circadian variation of mouse aqueous humor protein.Mol Vis. 2006 Jun 1;12:639-43. Mol Vis. 2006. PMID: 16785852
-
The Role of Beta-Adrenergic Receptors in the Regulation of Circadian Intraocular Pressure Rhythm in Mice.Curr Eye Res. 2017 Jul;42(7):1013-1017. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2016.1264605. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Curr Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28121174
-
Direct effect of light on 24-h variation of aqueous humor protein concentration in Sprague-Dawley rats.Exp Eye Res. 2008 Nov;87(5):487-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.08.015. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18822284 Free PMC article.
-
Diurnal and 24-h Intraocular Pressures in Glaucoma: Monitoring Strategies and Impact on Prognosis and Treatment.Adv Ther. 2018 Nov;35(11):1775-1804. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0812-z. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Adv Ther. 2018. PMID: 30341506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian rhythm of intraocular pressure.J Glaucoma. 1998 Apr;7(2):141-7. J Glaucoma. 1998. PMID: 9559503 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between biomechanical responses of posterior sclera and IOP elevations during micro intraocular volume change.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Nov 1;54(12):7215-22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12441. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24130185 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor GRβ regulates glucocorticoid-induced ocular hypertension in mice.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 16;8(1):862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19262-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29339763 Free PMC article.
-
Using genetic mouse models to gain insight into glaucoma: Past results and future possibilities.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Dec;141:42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26116903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeatability, reproducibility, and agreement of three tonometers for measuring intraocular pressure in rabbits.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 28;11(1):19217. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98762-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34584185 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Smart Pump for Monitoring and Controlling Intraocular Pressure.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Apr;45(4):990-1002. doi: 10.1007/s10439-016-1735-y. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27679446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu JH. Circadian rhythm of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 1998;7:141–7. - PubMed
-
- Liu JH. Diurnal measurement of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 2001;10:S39–41. - PubMed
-
- Schnell CR, Debon C, Percicot CL. Measurement of intraocular pressure by telemetry in conscious, unrestrained rabbits. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:958–65. - PubMed
-
- McLaren JW, Brubaker RF, FitzSimon JS. Continuous measurement of intraocular pressure in rabbits by telemetry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:966–75. - PubMed
-
- Percicot CL, Schnell CR, Debon C, Hariton C. Continuous intraocular pressure measurement by telemetry in alpha-chymotrypsin-induced glaucoma model in the rabbit: effects of timolol, dorzolamide, and epinephrine. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1996;36:223–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
