Orexigenic hormone ghrelin attenuates local and remote organ injury after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion
- PMID: 18431503
- PMCID: PMC2295264
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002026
Orexigenic hormone ghrelin attenuates local and remote organ injury after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion
Abstract
Background: Gut ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is a serious condition in intensive care patients. Activation of immune cells adjacent to the huge endothelial cell surface area of the intestinal microvasculature produces initially local and then systemic inflammatory responses. Stimulation of the vagus nerve can rapidly attenuate systemic inflammatory responses through inhibiting the activation of macrophages and endothelial cells. Ghrelin, a novel orexigenic hormone, is produced predominately in the gastrointestinal system. Ghrelin receptors are expressed at a high density in the dorsal vagal complex of the brain stem. In this study, we investigated the regulation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway by the novel gastrointestinal hormone, ghrelin, after gut I/R.
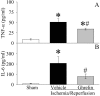
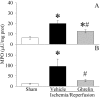
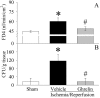
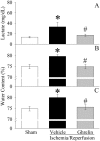
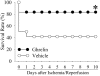
Methods and findings: Gut ischemia was induced by placing a microvascular clip across the superior mesenteric artery for 90 min in male adult rats. Our results showed that ghrelin levels were significantly reduced after gut I/R and that ghrelin administration inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokine release, reduced neutrophil infiltration, ameliorated intestinal barrier dysfunction, attenuated organ injury, and improved survival after gut I/R. Administration of a specific ghrelin receptor antagonist worsened gut I/R-induced organ injury and mortality. To determine whether ghrelin's beneficial effects after gut I/R require the intact vagus nerve, vagotomy was performed in sham and gut I/R animals immediately prior to the induction of gut ischemia. Our result showed that vagotomy completely eliminated ghrelin's beneficial effect after gut I/R. To further confirm that ghrelin's beneficial effects after gut I/R are mediated through the central nervous system, intracerebroventricular administration of ghrelin was performed at the beginning of reperfusion after 90-min gut ischemia. Our result showed that intracerebroventricular injection of ghrelin also protected the rats from gut I/R injury.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that ghrelin attenuates excessive inflammation and reduces organ injury after gut I/R through activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
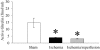



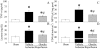
Similar articles
-
Orexigenic hormone ghrelin ameliorates gut barrier dysfunction in sepsis in rats.Crit Care Med. 2009 Aug;37(8):2421-6. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a557a2. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19531942 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin attenuates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by activating the mTOR signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Oct;32(4):851-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1452. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23877278
-
Effects of peripherally and centrally applied ghrelin in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion induced injury of the small intestine.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;62(4):429-39. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22100844
-
The controversial role of the vagus nerve in mediating ghrelin's actions: gut feelings and beyond.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Mar 12;12:228-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.03.003. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35746965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of ghrelin in the regulation of inflammation.FASEB J. 2022 Sep;36(9):e22508. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200634R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35983825 Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture and regulation of gastrointestinal function.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 21;21(27):8304-13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8304. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26217082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin Response to Acute and Chronic Exercise: Insights and Implications from a Systematic Review of the Literature.Sports Med. 2021 Nov;51(11):2389-2410. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01518-6. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34374968 Free PMC article.
-
Orexigenic hormone ghrelin ameliorates gut barrier dysfunction in sepsis in rats.Crit Care Med. 2009 Aug;37(8):2421-6. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a557a2. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19531942 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ghrelin supplementation on the acute phase of Chagas disease in rats.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Nov 9;12(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3787-y. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31706334 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: Drawing on Findings From Critical Illness to Explain Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 8;9:818728. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.818728. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35345768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oldenburg WA, Lau LL, Rodenberg TJ, Edmonds HJ, Burger CD. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia: A Clinical Review. Arch Int Med. 2004;164:1054–1062. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature. 2003;421:384–388. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002;420:853–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

