Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice
- PMID: 18431508
- PMCID: PMC2323186
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32691
Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice
Abstract
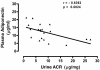
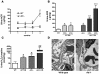
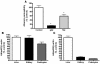
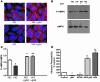
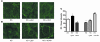
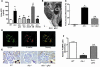
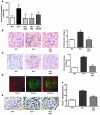
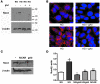
Increased albuminuria is associated with obesity and diabetes and is a risk factor for cardiovascular and renal disease. However, the link between early albuminuria and adiposity remains unclear. To determine whether adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived hormone, is a communication signal between adipocytes and the kidney, we performed studies in a cohort of patients at high risk for diabetes and kidney disease as well as in adiponectin-knockout (Ad(-/-)) mice. Albuminuria had a negative correlation with plasma adiponectin in obese patients, and Ad(-/-) mice exhibited increased albuminuria and fusion of podocyte foot processes. In cultured podocytes, adiponectin administration was associated with increased activity of AMPK, and both adiponectin and AMPK activation reduced podocyte permeability to albumin and podocyte dysfunction, as evidenced by zona occludens-1 translocation to the membrane. These effects seemed to be caused by reduction of oxidative stress, as adiponectin and AMPK activation both reduced protein levels of the NADPH oxidase Nox4 in podocytes. Ad(-/-) mice treated with adiponectin exhibited normalization of albuminuria, improvement of podocyte foot process effacement, increased glomerular AMPK activation, and reduced urinary and glomerular markers of oxidant stress. These results suggest that adiponectin is a key regulator of albuminuria, likely acting through the AMPK pathway to modulate oxidant stress in podocytes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Linking adiponectin to proteinuria.J Clin Invest. 2008 May;118(5):1619-22. doi: 10.1172/JCI35655. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18431507 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL051547/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 71360/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL 051547/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL051586/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK076133/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063018/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 053867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL 51586/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071360/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK046107/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 63018/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 076133/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046107/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

