Ablation of GalNAc-4-sulfotransferase-1 enhances reproduction by altering the carbohydrate structures of luteinizing hormone in mice
- PMID: 18431515
- PMCID: PMC2323185
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32467
Ablation of GalNAc-4-sulfotransferase-1 enhances reproduction by altering the carbohydrate structures of luteinizing hormone in mice
Abstract
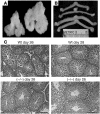
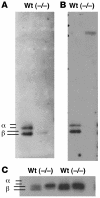
Luteinizing hormone (LH), produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary, is a member of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis that is required for production of the sex hormones estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone. Perturbations in levels of hormones associated with this axis can result in defects in sexual development and maturity. LH bears unique N-linked carbohydrate units that terminate with a sulfated N-acetylgalactosamine structure (GalNAc-4-SO(4)) that mediates its clearance from the blood. To determine the significance of this terminal structure, we ablated the gene encoding the sulfotransferase responsible for sulfate addition to GalNAc on LH, GalNAc-4-sulfotransferase-1 (GalNAc-4-ST1) in mice. Mice lacking GalNAc-4-ST1 exhibited increased levels of circulating LH. In male mice, this resulted in elevated levels of testosterone and precocious maturation of testis and seminal vesicles. Female mice lacking GalNAc-4-ST1 demonstrated elevated estrogen levels and exhibited precocious sexual maturation and increased fecundity. Female mice remained in estrus for prolonged periods and produced almost 50% more litters per mouse than wild-type mice over the same period of time. Thus, sulfate modification of the terminal glycosylation of LH plays a central role in regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis in vivo.
Figures

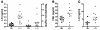




References
-
- Ying S.Y. Inhibins, activins, and follistatins: gonadal proteins modulating the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocr. Rev. 1988;9:267–293. - PubMed
-
- Strauss, J.F., 3rd, and Penning, T.M. 1999. Synthesis of the sex steroid hormones: molecular and structural biology with applications to clinical practise. InMolecular biology in reproductive medicine. B.C.J.M. Fauser, A.J. Rutherford, J.F. Strauss, 3rd, and A. Van Steirteghem, editors. The Parthenon Publishing Group. Carnforth, United Kingdom. 201–232.
-
- Bousfield, G.R., Perry, W.M., and Ward, D.N. 1994. Gonadotropins. Chemistry and biosynthesis. InThe physiology of reproduction. E. Knobil, and J.D. Neill, editors. Raven Press. New York, New York, USA. 1749–1792.
-
- Clarke I.J., Cummins J.T. The temporal relationship between gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion in ovariectomized ewes. Endocrinology. 1982;111:1737–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

