Draper-dependent glial phagocytic activity is mediated by Src and Syk family kinase signalling
- PMID: 18432193
- PMCID: PMC2493287
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06901
Draper-dependent glial phagocytic activity is mediated by Src and Syk family kinase signalling
Abstract
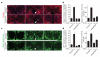
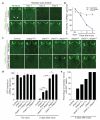
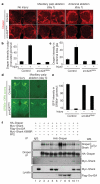
The cellular machinery promoting phagocytosis of corpses of apoptotic cells is well conserved from worms to mammals. An important component is the Caenorhabditis elegans engulfment receptor CED-1 (ref. 1) and its Drosophila orthologue, Draper. The CED-1/Draper signalling pathway is also essential for the phagocytosis of other types of 'modified self' including necrotic cells, developmentally pruned axons and dendrites, and axons undergoing Wallerian degeneration. Here we show that Drosophila Shark, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase similar to mammalian Syk and Zap-70, binds Draper through an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) in the Draper intracellular domain. We show that Shark activity is essential for Draper-mediated signalling events in vivo, including the recruitment of glial membranes to severed axons and the phagocytosis of axonal debris and neuronal cell corpses by glia. We also show that the Src family kinase (SFK) Src42A can markedly increase Draper phosphorylation and is essential for glial phagocytic activity. We propose that ligand-dependent Draper receptor activation initiates the Src42A-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Draper, the association of Shark and the activation of the Draper pathway. These Draper-Src42A-Shark interactions are strikingly similar to mammalian immunoreceptor-SFK-Syk signalling events in mammalian myeloid and lymphoid cells. Thus, Draper seems to be an ancient immunoreceptor with an extracellular domain tuned to modified self, and an intracellular domain promoting phagocytosis through an ITAM-domain-SFK-Syk-mediated signalling cascade.
Figures
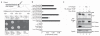
References
-
- Keegan K, Cooper JA. Use of the two hybrid system to detect the association of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase, SHPTP2, with another SH2-containing protein, Grb7. Oncogene. 1996;12:1537–1544. - PubMed
-
- Lioubin MN, et al. p150Ship, a signal transduction molecule with inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase activity. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1084–1095. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Yeung YG, Stanley ER. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a common 57-kDa protein in growth factor-stimulated and-transformed cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:6808–6814. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Z, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR. CED-1 is a transmembrane receptor that mediates cell corpse engulfment in C. elegans. Cell. 2001;104:43–56. - PubMed
-
- Freeman MR, Delrow J, Kim J, Johnson E, Doe CQ. Unwrapping glial biology. Gcm target genes regulating glial development, diversification, and function. Neuron. 2003;38:567–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

