Validation of three-dimensional model-based tibio-femoral tracking during running
- PMID: 18434230
- PMCID: PMC2668117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.03.003
Validation of three-dimensional model-based tibio-femoral tracking during running
Abstract
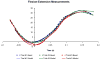
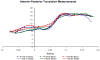
The purpose of this study was to determine the accuracy of a radiographic model-based tracking technique that measures the three-dimensional in vivo motion of the tibio-femoral joint during running. Tantalum beads were implanted into the femur and tibia of three subjects and computed tomography (CT) scans were acquired after bead implantation. The subjects ran 2.5m/s on a treadmill positioned within a biplane radiographic system while images were acquired at 250 frames per second. Three-dimensional implanted bead locations were determined and used as a "gold standard" to measure the accuracy of the model-based tracking. The model-based tracking technique optimized the correlation between the radiographs acquired via the biplane X-ray system and digitally reconstructed radiographs created from the volume-rendered CT model. Accuracy was defined in terms of measurement system bias, precision and root-mean-squared (rms) error. Results were reported in terms of individual bone tracking and in terms of clinically relevant tibio-femoral joint translations and rotations (joint kinematics). Accuracy for joint kinematics was as follows: model-based tracking measured static joint orientation with a precision of 0.2 degrees or better, and static joint position with a precision of 0.2mm or better. Model-based tracking precision for dynamic joint rotation was 0.9+/-0.3 degrees , 0.6+/-0.3 degrees , and 0.3+/-0.1 degrees for flexion-extension, external-internal rotation, and ab-adduction, respectively. Model-based tracking precision when measuring dynamic joint translation was 0.3+/-0.1mm, 0.4+/-0.2mm, and 0.7+/-0.2mm in the medial-lateral, proximal-distal, and anterior-posterior direction, respectively. The combination of high-speed biplane radiography and volumetric model-based tracking achieves excellent accuracy during in vivo, dynamic knee motion without the necessity for invasive bead implantation.
Figures

References
-
- Karrholm J, Selvik G, Elmqvist L, Hansson L, Jonsson H. Three-dimensional instability of the anterior cruciate deficient knee. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (Br) 1988;70-B:777–783. - PubMed
-
- Selvik G. Roentgen Stereophotogrammetric Analysis. Acta Radiol. 1990;31:113–126. - PubMed
-
- Tashman S, Collon D, Anderson K, Kolowich P, Anderst W. Abnormal rotational knee motion during running after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2004;32(4):975–983. - PubMed
-
- Berhonnaud E, Herzberg G, Zhao K, An K, Dimnet J. Three-dimensional in vivo displacements of the shoulder complex from biplanar radiography. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005;27:214–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

