Unusually high prevalence of panton-valentine leukocidin genes among methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus strains carried in the Indonesian population
- PMID: 18434555
- PMCID: PMC2446829
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01173-07
Unusually high prevalence of panton-valentine leukocidin genes among methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus strains carried in the Indonesian population
Abstract
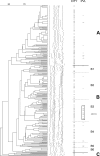
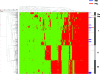
Few data on the molecular characteristics and epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus from Indonesia are available. The purpose of the present study was to define S. aureus reservoirs in both the Indonesian community and hospital using a collection of 329 nasal carriage isolates obtained during a survey of 3,995 healthy individuals and patients from Java, Indonesia. Only one strain (0.3%) was identified as methicillin-resistant S. aureus by mecA gene PCR. The Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) genes were detected in 35 methicillin-sensitive S. aureus strains (10.6%). Molecular typing by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of the 329 isolates showed extensive genetic diversity among both PVL-positive and PVL-negative strains. In Surabaya, Indonesia, however, a cluster was identified that was strongly associated with the presence of the PVL locus (P < 0.0001). As determined by high-throughput amplified fragment length polymorphism, PVL-positive strains occurred throughout all major AFLP clusters (I to IV). Multilocus sequence typing of a subset of isolates showed that most PVL-positive strains belonged to sequence type (ST) 188, while most PVL-negative isolates belonged to ST45. The high prevalence of PVL-positive S. aureus strains in certain regions of Indonesia is of concern since these strains may cause severe infections in the community and in hospitals.
Figures
References
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 3591819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Boye, K., M. D. Bartels, I. S. Andersen, J. A. Moller, and H. Westh. 2007. A new multiplex PCR for easy screening of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus SCCmec types I-V. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 13725-727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

