Quality control assessment of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) viral load quantification assays: results from an international collaboration on HIV-2 infection in 2006
- PMID: 18434556
- PMCID: PMC2446851
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00126-08
Quality control assessment of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) viral load quantification assays: results from an international collaboration on HIV-2 infection in 2006
Abstract
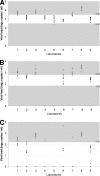
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) RNA quantification assays used in nine laboratories of the ACHI(E)V(2E) (A Collaboration on HIV-2 Infection) study group were evaluated. In a blinded experimental design, laboratories quantified three series of aliquots of an HIV-2 subtype A strain, each at a different theoretical viral load. Quantification varied between laboratories, and international standardization of quantification assays is strongly needed.
Figures
References
-
- Anonymous. 1994. Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results—part 2: basic method for the determination of repeatability and reproducibility of a standard measurement method. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Ferns, R. B., and J. A. Garson. 2006. Development and evaluation of a real-time RT-PCR assay for quantification of cell-free human immunodeficiency virus type 2 using a brome mosaic virus internal control. J. Virol. Methods 135102-108. - PubMed
-
- Kanki, P. J., K. U. Travers, S. MBoup, C. C. Hsieh, R. G. Marlink, N. A. Gueye, T. Siby, I. Thior, M. Hernandez-Avila, J. L. Sankale, et al. 1994. Slower heterosexual spread of HIV-2 than HIV-1. Lancet 343943-946. - PubMed
-
- Matheron, S., S. Pueyo, F. Damond, F. Simon, A. Lepretre, P. Campa, R. Salamon, G. Chene, and F. Brun-Vezinet. 2003. Factors associated with clinical progression in HIV-2-infected patients: the French ANRS cohort. AIDS 172593-2601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

