Coat-tether interaction in Golgi organization
- PMID: 18434597
- PMCID: PMC2441675
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1236
Coat-tether interaction in Golgi organization
Abstract
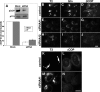
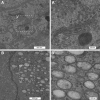
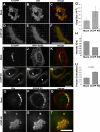
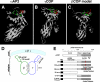
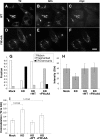
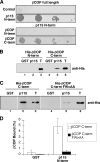
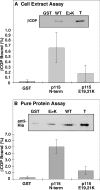
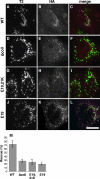
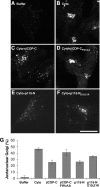
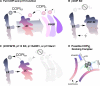
Biogenesis of the Golgi apparatus is likely mediated by the COPI vesicle coat complex, but the mechanism is poorly understood. Modeling of the COPI subunit betaCOP based on the clathrin adaptor AP2 suggested that the betaCOP C terminus forms an appendage domain with a conserved FW binding pocket motif. On gene replacement after knockdown, versions of betaCOP with a mutated FW motif or flanking basic residues yielded a defect in Golgi organization reminiscent of that occurring in the absence of the vesicle tether p115. Indeed, betaCOP bound p115, and this depended on the betaCOP FW motif. Furthermore, the interaction depended on E(19)E(21) in the p115 head domain and inverse charge substitution blocked Golgi biogenesis in intact cells. Finally, Golgi assembly in permeabilized cells was significantly reduced by inhibitors containing intact, but not mutated, betaCOP FW or p115 EE motifs. Thus, Golgi organization depends on mutually interacting domains in betaCOP and p115, suggesting that vesicle tethering at the Golgi involves p115 binding to the COPI coat.
Figures
Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 19:2681.
Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of betaCOP (Sec26p) identifies an appendage domain critical for function.BMC Cell Biol. 2008 Jan 22;9:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-9-3. BMC Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18211691 Free PMC article.
-
A cryptic Rab1-binding site in the p115 tethering protein.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 8;280(27):25840-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503925200. Epub 2005 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15878873
-
The interaction of two tethering factors, p115 and COG complex, is required for Golgi integrity.Traffic. 2007 Mar;8(3):270-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00530.x. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17274799
-
A role for giantin in docking COPI vesicles to Golgi membranes.J Cell Biol. 1998 Mar 9;140(5):1013-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.5.1013. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9490716 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a functional domain within the p115 tethering factor that is required for Golgi ribbon assembly and membrane trafficking.J Cell Sci. 2012 Apr 15;125(Pt 8):1896-909. doi: 10.1242/jcs.090571. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22328511 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SCYL1 arginine methylation by PRMT1 is essential for neurite outgrowth via Golgi morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Aug 15;31(18):1963-1973. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-02-0100. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32583741 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle tethering by a homotypic PDZ interaction underlies formation of the Golgi membrane network.J Cell Biol. 2009 Jul 13;186(1):41-55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200902110. Epub 2009 Jul 6. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19581411 Free PMC article.
-
Post-ER Stress Biogenesis of Golgi Is Governed by Giantin.Cells. 2019 Dec 13;8(12):1631. doi: 10.3390/cells8121631. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31847122 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving understanding of COPI vesicle formation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;10(5):360-4. doi: 10.1038/nrm2663. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19293819 Review.
-
Immuno-proteomics: Development of a novel reagent for separating antibodies from their target proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1854(6):592-600. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.10.011. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25466873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan B. B., Moyer B. D., Balch W. E. Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science. 2000;289:444–448. - PubMed
-
- Andag U., Neumann T., Schmitt H. D. The coatomer-interacting protein Dsl1p is required for Golgi-to-endoplasmic reticulum retrieval in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:39150–39160. - PubMed
-
- Andag U., Schmitt H. D. Dsl1p, an essential component of the Golgi-endoplasmic reticulum retrieval system in yeast, uses the same sequence motif to interact with different subunits of the COPI vesicle coat. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:51722–51734. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C., Hauri H. P. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J. Cell Sci. 2006;119:2173–2183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

