GRASP55 regulates Golgi ribbon formation
- PMID: 18434598
- PMCID: PMC2441664
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-11-1200
GRASP55 regulates Golgi ribbon formation
Abstract
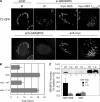
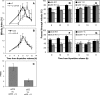
Recent work indicates that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)1 signaling at the G2/M cell cycle transition unlinks the contiguous mammalian Golgi apparatus and that this regulates cell cycle progression. Here, we sought to determine the role in this pathway of Golgi reassembly protein (GRASP)55, a Golgi-localized target of MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation at mitosis. In support of the hypothesis that GRASP55 is inhibited in late G2 phase, causing unlinking of the Golgi ribbon, we found that HeLa cells depleted of GRASP55 show a fragmented Golgi similar to control cells arrested in G2 phase. In the absence of GRASP55, Golgi stack length is shortened but Golgi stacking, compartmentalization, and transport seem normal. Absence of GRASP55 was also sufficient to suppress the requirement for MEK1 in the G2/M transition, a requirement that we previously found depends on an intact Golgi ribbon. Furthermore, mimicking mitotic phosphorylation of GRASP55 by using aspartic acid substitutions is sufficient to unlink the Golgi apparatus in a gene replacement assay. Our results implicate MEK1/ERK regulation of GRASP55-mediated Golgi linking as a control point in cell cycle progression.
Figures



References
-
- Allan V. J., Thompson H. M., McNiven M. A. Motoring around the Golgi. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E236–E242. - PubMed
-
- Angata K., Lee W., Mitoma J., Marth J. D., Fukuda M. Cellular and molecular analysis of neural development of glycosyltransferase gene knockout mice. Methods Enzymol. 2006;417:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Bachert C., Fimmel C., Linstedt A. D. Endosomal trafficking and proprotein convertase cleavage of cis Golgi protein GP73 produces marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Traffic. 2007;8:1415–1423. - PubMed
-
- Barr F. A., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J., Warren G. GRASP65, a protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1997;91:253–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

